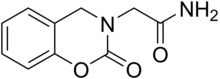
Caroxazone
 | |
| Dữ liệu lâm sàng | |
|---|---|
| Danh mục cho thai kỳ |
|
| Dược đồ sử dụng | Oral |
| Mã ATC |
|
| Tình trạng pháp lý | |
| Tình trạng pháp lý |
|
| Các định danh | |
Tên IUPAC
| |
| Số đăng ký CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Định danh thành phần duy nhất | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.481 |
| Dữ liệu hóa lý | |
| Công thức hóa học | C10H10N2O3 |
| Khối lượng phân tử | 206.20 g/mol |
| Mẫu 3D (Jmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Caroxazone (Surodil, Timostenil) là thuốc chống trầm cảm trước đây được sử dụng để điều trị trầm cảm nhưng hiện không còn được bán trên thị trường.[1][2] Nó hoạt động như một chất ức chế monoamin oxydase có thể đảo ngược (RIMA) của cả hai phân nhóm MAO-A và MAO-B, với ưu tiên gấp năm lần cho loại thứ hai.[3][4][5][6][7]
Tổng hợp[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]

Tổng hợp bắt đầu bằng cách khử hóa salicylaldehyd và glycinamide để cho 3. Quá trình tổng hợp được hoàn thành bằng phản ứng với phosgene và NaHCO3.
Xem thêm[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
- Paraxazone, một đồng phân của Caroxazone
Tham khảo[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
- ^ Dictionary of organic compounds. London: Chapman & Hall. 1996. ISBN 0-412-54090-8.
- ^ Cecchini, S; Petri, P; Ardito, R; Bareggi, S. R.; Torriti, A (1978). “A comparative double-blind trial of the new antidepressant caroxazone and amitriptyline”. The Journal of International Medical Research. 6 (5): 388–94. PMID 359383.
- ^ Monoamine oxidase inhibitors in neurological diseases. New York: M. Dekker. 1994. ISBN 0-8247-9082-0.
- ^ Moretti, A; Caccia, C; Martini, A; Bonollo, L; Amico, A; Sega, R; Nicolella, V; Nicolis, F. B. (tháng 5 năm 1981). “Effect of caroxazone, a new antidepressant drug, on monoamine oxidases in healthy volunteers”. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 11 (5): 511–5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01158.x. PMC 1401585. PMID 7272163.
- ^ Moretti, A; Caccia, C; Calderini, G; Menozzi, M; Amico, A (tháng 10 năm 1981). “Studies on the mechanism of action of caroxazone, a new antidepressant drug”. Biochemical Pharmacology. 30 (19): 2728–31. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(81)90549-9. PMID 6170295.
- ^ Martini, A; Bonollo, L; Nicolis, F. B.; Sega, R; Palermo, A (tháng 6 năm 1981). “Effects of caroxazone, a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor, on the pressor response to oral tyramine in man”. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 11 (6): 611–5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01178.x. PMC 1402186. PMID 7272178.
- ^ Martini, A; Bonollo, L; Nicolis, F. B.; Sega, R; Palermo, A; Braibanti, E (tháng 6 năm 1981). “Effects of caroxazone, a reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor, on the pressor response to intravenous tyramine in man”. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 11 (6): 605–10. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01177.x. PMC 1402193. PMID 7272177.
- ^ Bernardi, L; Coda, S; Nicolella, V; Vicario, G. P.; Gioia, B; Minghetti, A; Vigevani, A; Arcamone, F (1979). “Radioisotopic and synthetic studies related to caroxazone metabolism in man”. Arzneimittel-Forschung. 29 (9): 1412–6. PMID 583252.
- ^ Bernardi, L; Coda, S; Pegrassi, L; Suchowsky, G. K. (1968). “Pharmacological properties of some derivatives of 1,3-benzoxazine”. Experientia. 24 (8): 774–5. doi:10.1007/bf02144859. PMID 5683159.
- ^ Bernardi, L; Coda, S; Bonsignori, A; Pegrassi, L; Suchowsky, G. K. (1969). “Central depressant properties of 3,1-benzoxazine derivates”. Experientia. 25 (8): 787–8. doi:10.1007/bf01897874. PMID 5348526.
- ^ Đăng ký phát minh {{{country}}} {{{number}}}, "{{{title}}}", trao vào [[{{{gdate}}}]]; L. Bernardi et al., Bằng sáng chế Hoa Kỳ số 3.427.313 (1965, 1969 both to Soc. Farma. Italia).
