Khác biệt giữa bản sửa đổi của “Viêng Chăn (tỉnh)”
n clean up, replaced: {{Otheruses → {{bài cùng tên using AWB |
Không có tóm lược sửa đổi |
||
| Dòng 1: | Dòng 1: | ||
{{hatnote|This article is about the province. For other administrative entities see [[Vientiane|Vientiane City]] and [[Vientiane Prefecture]].}} |
|||
{{bài cùng tên|Viêng Chăn (định hướng)}} |
|||
{{Infobox settlement |
|||
{| border="1" cellpadding="2" cellspacing="0" align="right" |
|||
| name = {{raise|0.2em|Vientiane}} |
|||
! colspan="2" align=center bgcolor="#DEFFAD"|Thông tin |
|||
| native_name = {{lower|0.2em|{{nobold|ແຂວງວຽງຈັນ}}}} |
|||
| native_name_lang = lo |
|||
| settlement_type = [[Provinces of Laos|Province]] |
|||
| image_skyline = Montage of Vientiane Province, Laos (2013).jpg |
|||
| image_caption = |
|||
| image_alt = |
|||
| image_map = Map of Vientiane Province, Laos.jpg |
|||
| map_caption = Map of Vientiane Province |
|||
| map_alt = Map of Vientiane Province |
|||
| image_map1 = Vientiane Province-Laos.svg |
|||
| map_caption1 = Location of Vientiane Province in Laos |
|||
| map_alt1 = Map showing location of Vientiane Province in Laos |
|||
| coordinates = {{coord|18.8333|102.167|type:adm1st_region:KH|display=inline,title}} |
|||
| coordinates_footnotes = |
|||
| subdivision_type = [[List of sovereign states|Country]] |
|||
| subdivision_name = {{flag|Laos}} |
|||
| established_title = Established |
|||
| established_date = 1989 |
|||
| named_for = |
|||
| seat_type = Capital |
|||
| seat = [[Muang Phôn-Hông]] |
|||
| leader_party = |
|||
| leader_title = |
|||
| leader_name = |
|||
| area_footnotes = |
|||
| area_total_km2 = 15,927 |
|||
| area_note = |
|||
| elevation_footnotes = |
|||
| elevation_m = |
|||
| population_footnotes = |
|||
| population_total = 419090 |
|||
| population_as_of = 2015 census |
|||
| population_density_km2 = auto |
|||
| population_demonym = |
|||
| population_note = |
|||
| timezone1 = [[UTC+07]] |
|||
| postal_code_type = |
|||
| postal_code = |
|||
| iso_code = LA-VI |
|||
| website = |
|||
| footnotes = |
|||
}} |
|||
{{LaoText}} |
|||
'''Vientiane Province''' (also known as rural Vientiane) ([[Lao alphabet|Lao]] ແຂວງວຽງຈັນ) is a [[Provinces of Laos|province]] of [[Laos]], located in the northwest of the country. As of 2015 the province had a total population of 419,090 people. Vientiane Province is a large province, covering an area of {{convert|15927|km2}} with 10 districts in mid north-western Laos. The province borders [[Luang Prabang Province]] to the north, [[Xiangkhouang Province]] to the northeast, [[Bolikhamxai Province]] to the east, [[Vientiane Prefecture]] and [[Thailand]] to the south, and [[Xaignabouli Province]] to the west. The principal towns are [[Vang Vieng]] and [[Muang Phôn-Hông]]. Several kilometres to the south of Vang Vieng is one of Laos's largest lakes, [[Nam Ngum]]. Much of this area, particularly the forests of the southern part, are under the [[Phou Khao Khouay National Bio-Diversity Conservation Area]]. The principal rivers flowing through the province are the [[Nam Song River]], [[Nam Ngum River]] and the [[Nam Lik River]]. |
|||
In the mid-16th century, Vientiane under King Setthathirat's rule became prosperous. It became a major centre of Buddhist teachings and many wats were built.<ref name=Lonely>{{Cite web|url=http://www.lonelyplanet.com/laos/northern-laos/vientiane-province/history|title= Vientiane Province History |accessdate=30 November 2012|publisher=Lonely Planet}}</ref> |
|||
In 1989, the province was split into two halves — the [[Vientiane Prefecture]] containing the city [[Vientiane]] itself, and the remaining province. |
|||
Since 2000, tourism in the region has rocketed, with many thousands visiting [[Vientiane]] and [[Vang Vieng]] every year. In recent years, new investment has gone into the suburbs of Vientiane. |
|||
==History== |
|||
The great Laotian epic, the [[Phra Lak Phra Lam]], claims that Prince Thattaradtha founded the city when he left the legendary Lao kingdom of ''Muong Inthapatha Maha Nakhone'' because he was denied the throne in favor of his younger brother.{{sfn|Fanthorpe|2009|p=66}} Thattaradtha founded a city called ''Maha Thani Si Phan Phao'' on the western banks of the [[Mekong|Mekong River]]; this city was said to have later become today's [[Udon Thani]], [[Thailand]].{{sfn|Võ|1972|p=21}} One day, a seven-headed [[Naga (mythology)|Naga]] told Thattaradtha to start a new city on the eastern bank of the river opposite ''Maha Thani Si Phan Phao''.{{sfn|Fanthorpe|2009|p=66}} The prince called this city ''Chanthabuly Si Sattanakhanahud''; which was said to be the predecessor of modern Vientiane.{{sfn|Võ|1972|p=21}} |
|||
Contrary to the Phra Lak Phra Ram, most historians believe that the city of Vientiane was an early [[Khmer Empire|Khmer]] settlement centered around a [[Hindu]] temple, which the Pha That Luang would later replace. Khmer princes ruling [[Say Fong]] were known to have made pilgrimages to the shrine near Vientiane.{{sfn|Askew, Logan & Long|2009|p=21}} In the 11th and 12th centuries, the time when the [[Lao people|Lao]] and [[Thai people]] are believed to have entered [[Southeast Asia]] from [[Southern China]], the few remaining Khmers in the area were either killed, removed, or assimilated into the Lao civilization, which would soon overtake the area.{{sfn|Grabowski|1995|p=111}} |
|||
In 1354, when [[Fa Ngum]] founded the kingdom of [[Lan Xang]], Vientiane became an important administrative city, even though it was not made the capital.{{sfn|Askew, Logan & Long|2009|p=37}} King [[Setthathirath]] officially established it as the capital of Lan Xang in 1563, to avoid a Burmese invasion.{{sfn|Grabowski|1995|p=111}} In the following several centuries Vientiane's position was not stable; at times it was strong and regional centre but many times it came under the control Vietnam, Burma and Siam.<ref name=Lonely/> |
|||
When Lan Xang fell apart in 1707, it became an independent [[Kingdom of Vientiane]].{{sfn|Kislenko|2009|p=24}} In 1779, it was conquered by the Siamese general Phraya [[Buddha Yodfa Chulaloke|Chakri]] and made a vassal of [[Thailand|Siam]].{{sfn|Grabowski|1995|p=111}} When King [[Anouvong]] tried to assert himself as an independent kingdom, and raised an unsuccessful rebellion, it was obliterated by [[Thai people|Siamese]] armies in 1827.{{sfn|Lee|2007|p=27}} The city was burned to the ground and was looted of nearly all Laotian artifacts, including Buddha statues and people.<ref name=Lonely/><ref name="Summary of World Broadcasts: Far East">{{cite book|title=Summary of World Broadcasts: Far East|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=etmZAAY73XEC|accessdate=30 November 2012|year=1987|publisher=Monitoring Service of the British Broadcasting Corporation}}</ref> The Siamese routed Anouvong and razed the city leaving only the [[Wat Si Saket]] in good shape, shifting all people.<ref name=Lonely/> Vientiane was in great disrepair, depopulated and disappearing into the forest, when the French arrived in 1867. It eventually passed to [[France|French]] rule in 1893. It became the capital of the French protectorate of Laos in 1899.{{sfn|Doeden|2007|p=30}} The French rebuilt the city and rebuilt or repaired Buddhist temples such as [[Pha That Luang]], [[Haw Phra Kaew]], and left many colonial buildings behind. By a decree signed in 1900 by Governor-General [[Paul Doumer]], the province was divided into four [[Canton (country subdivision)|''muang'']], these being Borikan, Patchoum, Tourakom, and Vientiane. Two years earlier, men from these four ''muang'' were responsible for building a house for the first administrator of [[Vientiane]], Pierre Morin.{{sfn|Askew, Logan & Long|2009|p=77}} |
|||
During [[World War II]], Vientiane fell with little resistance and was occupied by Japanese forces, under the command of [[Sako Masanori]]. On 9 March 1945 French paratroopers arrived, and "liberated" the Vientiane on April 24, 1945.{{sfn|Eur|2002|p=736}} |
|||
As the [[Laotian Civil War]] broke out between the [[Royal Lao Government]] and the [[Pathet Lao]], Vientiane became unstable. In August 1960, [[Kong Le]] seized the capital and insisted that [[Souvanna Phouma]], become Prime Minister. In mid-December, General Phoumi then seized the capital, overthrew the Phouma Government, and installed [[Boun Oum]] as Prime Minister. In mid-1975, Pathet Lao troops moved towards the city and American personnel began evacuating the capital. On August 23, 1975, a contingent of 50 Pathet Lao women, symbolically "liberated" the city.{{sfn|Eur|2002|p=736}} In December 2, 1975, the [[Communism|communist]] party of the [[Pathet Lao]] took over Vientiane and defeated the [[Kingdom of Laos]] which ended the [[Laotian Civil War]], but the ongoing [[Insurgency in Laos]] began in the jungle, with the Pathet Lao fighting the Hmongs, Royalist-in-exile and the Right-wings. |
|||
In the 1950s and 1960s during the [[French-Indo China War]] and [[Vietnam War]], thousands of refugees arrived in the province. By 1963, some 128,000 at arrived, especially [[Hmong people]] from [[Xiengkhouang Province]].{{sfn|Jong|Donovan|2007|p=80}} Some 150,000 more arrived in the early 1970s.{{sfn|Jong|Donovan|2007|p=80}} Many of the refugees arrived were addicted to [[opium]].{{sfn|Westermeyer|1983|p=203}} In 1989, the province was split into two parts, the [[Vientiane Prefecture]], which contains the capital, [[Vientiane]], and the remaining area, the Vientiane Province. |
|||
In late 2006, 13 ethnic [[Khmu people|Khmu]] Christians were arrested in the village of [[Khon Kean]]. One was released in April 2007, and on May 16, nine others were released after being held at a police detention facility in [[Hin Heup]].{{sfn|Államok|2007|p=865}} Vientiane hosted the [[2009 Southeast Asian Games|25th Southeast Asian Games]] in December 2009 celebrating the 50 years of [[SEA Games]]. The Xaysomboun region experiences sporadic violence between government forces and Hmong rebels.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.reuters.com/article/us-china-laos-attacks-idUSKBN19A09J |publisher=[[Reuters]] |title=China issues security alert in Laos after national shot dead |first=Michael |last=Martina |editor-first=Robert |editor-last=Birsel |quote=Laos' Xaysomboun region has been plagued by sporadic conflict between the government and ethnic Hmong rebels for years. |date=June 18, 2017}}</ref> |
|||
==Geography== |
|||
Vientiane Province, one of the provinces of Laos,<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www.laotourism.org/laotourism.htm|title=Home|work=Regions|accessdate=7 January 2013|publisher=Official website of Laos Tourism}}</ref> is a large province, covering an area of {{convert|15927|km2}} with 10 districtsin mid north-western Laos. The province borders [[Luang Prabang Province]] to the north, [[Xiangkhouang Province]] to the northeast, [[Bolikhamxai Province]] to the east, [[Vientiane Prefecture]] and [[Thailand]] to the south, and [[Xaignabouli Province]] to the west. The principal towns are [[Vang Vieng]] and [[Muang Phôn-Hông]]. Vang Vieng is connected to Vientiane, roughly {{convert|170|km}} by road to the south and [[Luang Prabang]] to the northwest by [[Route 13 (Laos)|Route 13]], the most important highway in the province, followed by [[Route 10 (Laos)|Route 10]].{{sfn|Lightner|2005|p=310}}<ref name="GM">{{cite map|title= Maps|publisher=[[Google Maps]]}}</ref> Most of the population of the province is situated in the towns and villages along and near Route 13; from the south to the north these include [[Ban Phonsoung]], [[Ban Saka]] and [[Toulakhom]] (along Route 10 east of Route 13), [[Ban Nalao]], [[Ban Nong Khay]], [[Ban Keng Kang]], [[Ban Vang Khay]], [[Ban Houay Pamon]], [[Ban Namone]], [[Vang Vieng]], [[Ban Nampo]], [[Ban Phatang]], [[Ban Bome Phek]], [[Ban Thieng]], [[Muang Kasi]] and [[Ban Nam San Noi]] near the border with Xiangkhouang Province.<ref name="GM"/> |
|||
Several kilometres to the south of Vang Vieng is one of Laos's largest lakes, [[Nam Ngum]]. Much of this area, particularly the forests of the southern part, are under the [[Phou Khao Khouay National Bio-Diversity Conservation Area]].<ref name="GM"/> To the east is the highest peak of Laos, [[Phou Bia]], a heavily forested hilly area, east of [[Ban Thamkalong]]. The principal rivers flowing through the province are the [[Nam Song River]], [[Nam Ngum River]] and the [[Nam Lik River]]. |
|||
<center> |
|||
<gallery widths="200px" heights="200px" perrow="4"> |
|||
File:VientianeProvince VangVieng3 tango7174.jpg|Vang Vieng centre |
|||
File:VientianeProvince VangVieng2 tango7174.jpg|Nam Song in Vang Vieng |
|||
File:VientianeProvince PhuPhra1 tango7174.jpg|Phu Phra mountain |
|||
File:VientianeProvince ThaHeua2 tango7174.jpg|Fish from the Nam Ngum |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
</center> |
|||
==Protected areas== |
|||
[[Phou Khao Khoay National Biodiversity Conservation Area]] is a [[protected area]] located {{convert|40|km}} northeast of Vientiane. It was established on 29 October 1993 covering an area of 2,000 km<sup>2</sup> extending into Khet Phiset Xaisomboon (Special Zone), Vientiane Prefecture and Vientiane Province. Its mountainous topography, with elevation varying from 200 m – 1761 m, emerged from "uplifting and exposure of the underlying sedimentary (Indosinias schist-clay-sandstone) complex". Sandstones are also seen spread in layers. extensive Flat uplands with sandstones with hardly any soil cover are also part of the topography of the park. It has a large stretch of mountain range with [[sandstone]] cliffs, river gorges and three large rivers with tributaries which flow into the Mekong River. It has monsoonal climate with recorded annual rainfall of 1936.1 mm (with higher reaches recording more rainfall). The mean annual temperature is 26.6 °C with recorded the mean maximum of 31.6 °C and the mean minimum temperature of 21.5 °C. The forests are evergreen, Shorea mixed deciduous forest, dry [[dipterocarp]] and pine type; particularly coniferous forest, of mono specific stands of ''[[Pinus merkusii]]'', ''[[Fokienia]] hodgsonsii'', [[bamboo]] (''mai sanod''), and fire-climax grasslands. Animals found here include [[elephant]]s, [[tiger]]s, [[bear]]s, 13 pairs of [[Nomascus|white-cheeked gibbons]], and [[langur]]s and many species of [[reptile]]s, [[amphibian]]s and birds. The [[green peafowl]] has been reported here, near Ban Nakhay and Ban Nakhan Thoung, although it was generally considered to be extinct in Laos; conservation management has increased its population.<ref name=Pou>{{Cite web|url=http://www.ecotourismlaos.com/phoukhaokhouay.htm|title= Phou Khao Khouay|accessdate=10 December 2012|publisher=Official Website of Ecotourism Organization}}</ref><ref name="NBCA">{{Cite web|url=http://www.ecotourismlaos.com/directory/protected_areas/phoukaokhouay.htm|title= Phou Khao Khouay NBCA|accessdate=10 December 2012|publisher=Official Website of Ecotourism Organization}}</ref> |
|||
[[Ban Na Reserve]] is a wildlife protected area where trekking is popular in its peripheral areas. The habitat is known for its bamboo, dense forest and wild elephants.<ref name="NBCA"/><ref name="LT"/> |
|||
The Mekong Channel upstream of Vientiane [[Important Bird Area]] (IBA) is 18,230 hectares in size. As its name implies it comprises an approximately {{convert|300|km}} section of the Mekong Channel upstream of Vientiane city. It is situated in two provinces: Vientiane and [[Sainyabuli Province|Sainyabuli]]. The topography features braided streams, bushland, gravel bars, open sandy islands, rock outcrops, and sand bars. Notable [[avifauna]] include [[great thick-knees]] (''Esacus recurvirostris''), [[Jerdon's bushchat]] (''Saxicola jerdoni''), [[river lapwing]] (''Vanellus duvaucelii''), [[small pratincole]] (''Glareola lactea''), and [[wire-tailed swallow]] (''Hirundo smithii'').<ref name="birdlife.orgLA006">{{cite web|url=http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/sitefactsheet.php?id=16630|title=Important Bird Areas factsheet: Mekong Channel upstream of Vientiane|year=2012|publisher=BirdLife International|accessdate=9 December 2012}}</ref> Around the village of [[Ban Sivilay]], a bird sanctuary has large flocks of [[whistling ducks]] and [[egrets]] roosting.<ref name="LT"/> |
|||
==Administrative divisions== |
|||
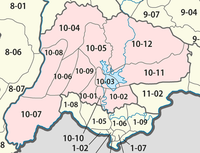
The province is made up of the following 10 districts:<ref name= Veint>{{Cite web|url=http://www.laotourism.org/vientiane%20province.htm|title= Destination: Vientiane Province|accessdate=10 December 2012|publisher= Official website of Laos Tourism Organization}}</ref> |
|||
{| class="wikitable" style="font-size:90%;" |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
! Map |
|||
|Tỉnh lỵ: ||[[Muang Phonhong]] |
|||
! Code |
|||
! Name |
|||
! Lao |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|rowspan=13|[[File:Vientiane Province districts.png|200px]] |
|||
|Diện tích: ||valign=top|15.927 [[kilômét vuông|km²]] |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
||10-01||Phonhong||{{lang|lo|ໂພນໂຮງ}} |
|||
|Dân số: ||valign=top|373.700 <small>''(2004)''</small> |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
||10-02||Thoulakhom||{{lang|lo|ທຸລະຄົມ}} |
|||
|[[Mật độ dân số]]: ||valign=top|23 người/km² |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
||10-03||Keo Oudom||{{lang|lo|ແກ້ວອຸດົມ}} |
|||
|[[ISO 3166-2]]: ||LA-VI |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
||10-04||Kasy||{{lang|lo|ກາສີ}} |
|||
|[[Geocode]]: ||1000 |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
||10-05||Vangvieng||{{lang|lo|ວັງວຽງ}} |
|||
!colspan="2" align=center bgcolor="#DEFFAD"|Bản đồ |
|||
|- |
|||
||10-06||Feuang||{{lang|lo|ເຟືອງ}} |
|||
|- |
|||
||10-07||Xanakharm||{{lang|lo|ຊະນະຄາມ}} |
|||
|- |
|||
||10-08||Mad||{{lang|lo|ແມດ}} |
|||
|- |
|||
||10-09||Hineherb||{{lang|lo|ຫີນເຫີບ}} |
|||
|- |
|||
||10-10||Viengkham||{{lang|lo|ວຽງຄໍາ}} |
|||
|- |
|||
||10–11||Meun||{{lang|lo|ໝື່ນ}} |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|colspan="2" align=center|[[Tập tin:Laos Vientiane province.png]] |
|||
|} |
|} |
||
'''Tỉnh Viêng Chăn''' ([[tiếng Lào]]: ແຂວງວຽງຈັນ) là một tỉnh của Lào, tọa lạc tại tây bắc [[Lào]]. |
|||
==Demographics== |
|||
Năm [[1989]] tỉnh này được tách ra làm hai phần - Đô thị đặc biệt Viêng Chăn và tỉnh Viêng Chăn còn lại. |
|||
Population figures for the province increased dramatically during the period between 1943 (23,200) to 1955 (45,000). The demographics for ethnic breakdown in 1943 were: Lao 41.5%; Vietnamese (Annamites) 53%; Chinese 4%; Others 1.5%.{{sfn|Askew, Logan & Long|2009|p=118}} The population last reported was 388,833, as of March 2005 census with [[Muang Phôn-Hông]] as its capital.<ref name= stat>{{Cite web|url=http://www.statoids.com/ula.html|title=Provinces of Laos |accessdate=1 November 2012|publisher=Statoids.com}}</ref> |
|||
==Economy== |
|||
Since 2000, tourism in the region has rocketed, with many thousands visiting [[Vientiane]] and [[Vang Vieng]] every year. In recent years, new investment has gone into the suburbs of Vientiane. A tile factory has been established in the village of [[Phai Lom, Laos|Phai Lom]] and a bio-organic fertilizer factory has been established in the village of [[Dong Xiengdy]]. Another tile factory has also been established in the village of [[Hathdeua]], [[Keo Oudom District]].{{sfn|Askew, Logan & Long|2009|p=118}} [[Lonely Planet]] said of the impact of tourism upon the town of Vang Vieng, "The growth of Vang Vieng has taken its toll. Inevitably the profile of the town has changed and the reason travelers first came here- to experience small-town Laos in a stunning setting – has been replaced by multistorey guesthouses. Even the local market has moved to a big, soulless slab of concrete north of the town.{{sfn|Burke|Vaisutis|2007|p=122}} In the “Ban Bo village of Thoulakhom District salt extraction is popular part time economic activity. The village is 60 kilometers from Vientiane and the extraction of salt is done by traditional methods.<ref name="LT"/> |
|||
Although tourism has grown rapidly, most rural peoples still depend upon agriculture for their livelihoods. The Vientiane Plain which covers Vientiane Province and Vientiane Municipality is one of the six major rice producing plains in Laos.{{sfn|Bennett|2004|p=77}} Crafts and tailoring also employs a significant number, and most rural villages in the province have tailors who make pants, shirts, mosquito nets and sheets.{{sfn|Firth|Yamey|1964|p=93}} Herb doctors and carpenters are also occupations for a select few in the villages.{{sfn|Firth|Yamey|1964|p=93}} In the village of [[Ban Bo]] in [[Thoulakhom District]] is a salt extraction plant, employing most of the inhabitants in traditional extraction methods.<ref name="LT">{{cite web|url=http://www.laotourism.org/region,%20destination.htm|title=Vientiane Province|publisher=Lao Tourism Organizataion|accessdate=30 November 2012}}</ref> |
|||
Major operating companies in the mineral sector, as of 2008, include: Padeang Industry Public Co. Ltd, Phu Bin Ming Ltd, Laos Cement Co. Ltd, Wanrong Cement I, and Barite Mining Co.{{sfn|Geological Survey|2010|14}} As of 2009, each of the 126 ministry offices in Vientiane had IT facilities, including "one server, 10 PCs, a teleconference room, and a local area network connected to the national e-government infrastructure."{{sfn|Akhtar|Hassan|Arinto|2009|p=244}} |
|||
==Landmarks== |
|||
There are numerous caves in the province, especially in the Vang Vieng area. Of note are the Patang, Patho Nokham, Vangxang and Tham Chang Caves. Vangxang Cave, also known as Elephant Court, contains the remains of an ancient sanctuary which preexisted the [[Lane Xang Kingdom]], and contains five pink sandstone sculptures and two great Buddha images.<ref name="LT"/> Vang Vieng contains several Buddhist temples dated to the 16th and 17th centuries; among them [[Wat Si Vieng Song]] (Wat That), [[Wat Kang]] and [[Wat Si Sum]] are of note.{{sfn|Burke|Vaisutis|2007|p=123}} [[Ecotourism]] is a significant contributor to the provincial economy, and [[Adventure Lao]] manages a [[kayaking]] operation on the [[Nam Song River]], [[Nam Ngum River]] and the [[Nam Lik River]], which enables tourists to pass many villages.<ref name="ETL">{{cite web|url=http://ecotourismlaos.com/vientiane.htm|title=Vientiane Province|work=Ecotourism Laos|author=The Lao National Tourism Administration|publisher=GMS Sustainable Tourism Development Project in Lao PDR|accessdate=1 December 2012}}</ref> There is an artificial lake near the village of [[Ban Sivilay]] village with a protected bird habitat.<ref name="ETL"/> Also of note is Ban Ilai market in [[Muang Naxaithong]], which sells basketry, pottery and other traditional crafts.<ref name="ETL"/> |
|||
Famous water falls seen in Phu Khao Khuay are Tat Xai (which has seven cascades), further downstream the Pha Xai (40 m fall) and Tat Luek.{{Sfn|Burke|2007|page=119}} |
|||
Wat Pha Bhat Phonson at Tha Pha Baht is a rocky formation where Buddha foot prints, reclining Buddha and a monastery with large ornamented stupa (built in 1933) are worshipped.{{Sfn|Burke|2007|page=119}} |
|||
Ban Pako village in the midst of thick forests, 55 km away from Vientiane has eco-lodges created over a 40 ha forest preserve, which is a tourist attraction. The houses in this village are made of bamboo thatch at an isolated location stated to have been a settlement 2000 years ago which has been attested by archaeological finds of artifacts. A [[wat]] and a water fall are also located here.{{Sfn|Burke|2007|pp=116–117}} |
|||
The [[Nam Ngum Dam|Nam Ngum Reservoir]] on the Nam Ngum River, within in the [[Nam Ngum Reserve]] is an important water resources project which extends over a water spread area of 1,280 hectares during the monsoon season.<ref name="NBCA"/> The lake provides for recreational activities such as boating and picnics.<ref name="LT"/> In the [[Ban Thalad]] village of Keo-Oudom District, about {{convert|80|km}} from Vientiane, floating restaurants and sporting activities are popular.<ref name="LT"/> |
|||
Among the many caves in the province, the [[Vangxang Cave]] also called the "Elephant Court" remnants of an ancient sanctuary of the Lane Xang Kingdom are seen. It is approachable along Route 13 (north) located at km 48, the cave has 5 large sculptures made of pink sandstone and also two massive images of Buddha.<ref name="LT"/> |
|||
The [[Thoulakhom]] Zoo houses exotic and rare animals of Laos.<ref name="LT"/> |
|||
==Hành chính== |
|||
<center> |
|||
Tỉnh này có các huyện sau: |
|||
<gallery widths="200px" heights="200px" perrow="4"> |
|||
File:VientianeProvince VangXang2 tango7174.jpg|Vang Xang |
|||
File:VientianeProvince VangVieng ThamJang3 tango7174.jpg|Tham Chang |
|||
File:VientianeProvince VangVieng VatSiViengSong3 tango7174.jpg|Wat Si Vieng Song |
|||
File:VientianeProvince VangVieng VatKang1 tango7174.jpg|Wat Kang |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
</center> |
|||
==References== |
|||
# [[Feuang]] (10-06) |
|||
{{commons}} |
|||
# [[Hinhurp]] (10-09) |
|||
{{Reflist|2}} |
|||
# [[Hom]] (10-11) |
|||
# [[Kasy]] (10-04) |
|||
# [[Keo Oudom]] (10-03) |
|||
# [[Mad]] (10-08) |
|||
# [[Phonhong]] (10-01) |
|||
# [[Thoulakhom]] (10-02) |
|||
# [[Vangvieng]] (10-05) |
|||
# [[Viengkham]] (10-10) |
|||
# [[Saisomboun]] (10-12) |
|||
# [[Xanakharm]] (10-07) |
|||
# [[Meun]] (10-13) |
|||
===Bibliography=== |
|||
[[Tập tin:Vientiane Province districts.png|nhỏ|trái|Các huyện của tỉnh Viêng Chăn]] |
|||
*{{cite book|last1=Akhtar|first1=Shahid|last2=Arinto|first2=Patricia B.|last3=Abu|first3=Hassan, Musa|title=Digital Review of Asia Pacific 2009–2010|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=R4u48rbqEe0C&pg=PA244|date=3 June 2009|publisher=IDRC|isbn=978-81-321-0084-3|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|author=Államok, Egyesült|title=Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2007|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=O5rs8UkMj64C&pg=PA865|publisher=Government Printing Office|page=865|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last1=Askew|first1=Marc|last2=Logan|first2=Williams S.|last3=Long|first3=Colin|title=Vientiane: Transformation of a Lao landscape|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DNJ_e6FKjrwC&pg=PA118|year=2009|publisher=Routledge|isbn=978-1-134-32365-4|pages=118–|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Bennett|first=J.|title=New Approaches to Gall Midge Resistance in Rice|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=QLsJdybyuNEC&pg=PA77|date=1 January 2004|publisher=Int. Rice Res. Inst.|isbn=978-971-22-0198-1|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last1=Burke|first1=Andrew|last2=Vaisutis|first2=Justine|title=Laos 6th Edition|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=jm4GBvwaF50C&pg=PA122|date=1 August 2007|publisher=Lonely Planet|isbn=978-1-74104-568-0|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Doeden|first=Matt|title=Laos in Pictures|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qkuSVaUuiVgC&pg=PA30|date=1 January 2007|publisher=Twenty-First Century Books|isbn=978-0-8225-6590-1|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|author=Eur|title=Far East and Australasia 2003|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=e5Az1lGCJwQC&pg=PA736|year=2002|publisher=Psychology Press|isbn=978-1-85743-133-9|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Fanthorpe|first=Lionel & Patricia|title=Secrets of the World's Undiscovered Treasures|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=xmkJmYkwMWAC&pg=PA66|date=23 March 2009|publisher=Dundurn|isbn=978-1-77070-384-1|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last1=Firth|first1=Raymond|last2=Yamey|first2=Basil S.|title=Capital, Saving & Credit in Peasant Societies|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1gLD--X_d4oC&pg=PA93|year=1964|publisher=Transaction Publishers|isbn=978-0-202-30918-7|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|author=Geological Survey (U S )|title=Minerals Yearbook: Area Reports: International 2008: Asia and the Pacific|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=DGuvgMVYS0wC&pg=SA14|date=25 October 2010|publisher=Government Printing Office|isbn=978-1-4113-2964-5|pages=14–|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Grabowsky|first=Volker|title=Regions and National Integration in Thailand, 1892–1992|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=FnuGAyNT2bUC&pg=PA111|year=1995|publisher=Otto Harrassowitz Verlag|isbn=978-3-447-03608-5|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last1=Jong|first1=Wil De|last2=Donovan|first2=Deanna|author3=Ken-ichi Abe|title=Extreme Conflict and Tropical Forests|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=e0YFDOzO1MoC&pg=PA80|date=5 March 2007|publisher=Springer|isbn=978-1-4020-5461-7|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Kislenko|first=Arne|title=Culture And Customs Of Laos|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=bCMgBlhtm8sC&pg=PR24|year=2009|publisher=ABC-CLIO|isbn=978-0-313-33977-6|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Lee|first=Jonathan H. X.|title=Laotians in the San Francisco Bay Area|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Nio4CnKO7CgC&pg=PA7|date=17 September 2012|publisher=The Center for Lao Studies, Arcadia Publishing|isbn=978-0-7385-9586-3|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Lightner, Jr|first=Sam |title=Thailand: A Climbing Guide|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=MNkTq1DGrR4C&pg=PA310|date=30 October 2005|publisher=The Mountaineers Books|isbn=978-0-89886-750-3|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Võ|first=Thu Tịnh|title=The Phra Lak-Phra Lam (The Lao version of the Ramayana).: Abridged translation of the manuscript of Vat Kang Tha|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=sK4OAAAAMAAJ|year=1972|publisher=Cultural Survey of Laos|ref=harv}} |
|||
*{{cite book|last=Westermeyer|first=Joseph|title=Poppies, Pipes, and People: Opium and Its Use in Laos|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=czd4aRDYQjsC&pg=PA203|year=1983|publisher=University of California Press|isbn=978-0-520-04622-1|ref=harv}} |
|||
{{Geographic location |
|||
{{Các tỉnh của Lào}} |
|||
|Centre = Vientiane Province |
|||
==Tham khảo== |
|||
|North = [[Luang Prabang Province]] |
|||
{{tham khảo}} |
|||
|Northeast = [[Xaisomboun Province]] |
|||
{{sơ khai địa lý}} |
|||
|East = [[Bolikhamsai Province]] |
|||
|Southeast = |
|||
|South = [[Vientiane Prefecture]] |
|||
|Southwest = [[Loei Province]], {{flag|Thailand}} |
|||
|West = [[Sainyabuli Province]] |
|||
|Northwest = |
|||
}} |
|||
[[Thể loại:Tỉnh Viêng Chăn| ]] |
[[Thể loại:Tỉnh Viêng Chăn| ]] |
||
Phiên bản lúc 16:55, ngày 1 tháng 12 năm 2017
| Vientiane ແຂວງວຽງຈັນ | |
|---|---|
| — Province — | |
 | |
 Map of Vientiane Province | |
 Location of Vientiane Province in Laos | |
| Country | |
| Established | 1989 |
| Capital | Muang Phôn-Hông |
| Diện tích | |
| • Tổng cộng | 15,927 km2 (6,149 mi2) |
| Dân số (2015 census) | |
| • Tổng cộng | 419.090 |
| • Mật độ | 26,000/km2 (68,000/mi2) |
| Múi giờ | UTC+07 |
| Mã điện thoại | 021 |
| Mã ISO 3166 | LA-VI |
Bản mẫu:LaoText Vientiane Province (also known as rural Vientiane) (Lao ແຂວງວຽງຈັນ) is a province of Laos, located in the northwest of the country. As of 2015 the province had a total population of 419,090 people. Vientiane Province is a large province, covering an area of 15.927 kilômét vuông (6.149 dặm vuông Anh) with 10 districts in mid north-western Laos. The province borders Luang Prabang Province to the north, Xiangkhouang Province to the northeast, Bolikhamxai Province to the east, Vientiane Prefecture and Thailand to the south, and Xaignabouli Province to the west. The principal towns are Vang Vieng and Muang Phôn-Hông. Several kilometres to the south of Vang Vieng is one of Laos's largest lakes, Nam Ngum. Much of this area, particularly the forests of the southern part, are under the Phou Khao Khouay National Bio-Diversity Conservation Area. The principal rivers flowing through the province are the Nam Song River, Nam Ngum River and the Nam Lik River.
In the mid-16th century, Vientiane under King Setthathirat's rule became prosperous. It became a major centre of Buddhist teachings and many wats were built.[1] In 1989, the province was split into two halves — the Vientiane Prefecture containing the city Vientiane itself, and the remaining province.
Since 2000, tourism in the region has rocketed, with many thousands visiting Vientiane and Vang Vieng every year. In recent years, new investment has gone into the suburbs of Vientiane.
History
The great Laotian epic, the Phra Lak Phra Lam, claims that Prince Thattaradtha founded the city when he left the legendary Lao kingdom of Muong Inthapatha Maha Nakhone because he was denied the throne in favor of his younger brother.[2] Thattaradtha founded a city called Maha Thani Si Phan Phao on the western banks of the Mekong River; this city was said to have later become today's Udon Thani, Thailand.[3] One day, a seven-headed Naga told Thattaradtha to start a new city on the eastern bank of the river opposite Maha Thani Si Phan Phao.[2] The prince called this city Chanthabuly Si Sattanakhanahud; which was said to be the predecessor of modern Vientiane.[3]
Contrary to the Phra Lak Phra Ram, most historians believe that the city of Vientiane was an early Khmer settlement centered around a Hindu temple, which the Pha That Luang would later replace. Khmer princes ruling Say Fong were known to have made pilgrimages to the shrine near Vientiane.[4] In the 11th and 12th centuries, the time when the Lao and Thai people are believed to have entered Southeast Asia from Southern China, the few remaining Khmers in the area were either killed, removed, or assimilated into the Lao civilization, which would soon overtake the area.[5]
In 1354, when Fa Ngum founded the kingdom of Lan Xang, Vientiane became an important administrative city, even though it was not made the capital.[6] King Setthathirath officially established it as the capital of Lan Xang in 1563, to avoid a Burmese invasion.[5] In the following several centuries Vientiane's position was not stable; at times it was strong and regional centre but many times it came under the control Vietnam, Burma and Siam.[1]
When Lan Xang fell apart in 1707, it became an independent Kingdom of Vientiane.[7] In 1779, it was conquered by the Siamese general Phraya Chakri and made a vassal of Siam.[5] When King Anouvong tried to assert himself as an independent kingdom, and raised an unsuccessful rebellion, it was obliterated by Siamese armies in 1827.[8] The city was burned to the ground and was looted of nearly all Laotian artifacts, including Buddha statues and people.[1][9] The Siamese routed Anouvong and razed the city leaving only the Wat Si Saket in good shape, shifting all people.[1] Vientiane was in great disrepair, depopulated and disappearing into the forest, when the French arrived in 1867. It eventually passed to French rule in 1893. It became the capital of the French protectorate of Laos in 1899.[10] The French rebuilt the city and rebuilt or repaired Buddhist temples such as Pha That Luang, Haw Phra Kaew, and left many colonial buildings behind. By a decree signed in 1900 by Governor-General Paul Doumer, the province was divided into four muang, these being Borikan, Patchoum, Tourakom, and Vientiane. Two years earlier, men from these four muang were responsible for building a house for the first administrator of Vientiane, Pierre Morin.[11]
During World War II, Vientiane fell with little resistance and was occupied by Japanese forces, under the command of Sako Masanori. On 9 March 1945 French paratroopers arrived, and "liberated" the Vientiane on April 24, 1945.[12] As the Laotian Civil War broke out between the Royal Lao Government and the Pathet Lao, Vientiane became unstable. In August 1960, Kong Le seized the capital and insisted that Souvanna Phouma, become Prime Minister. In mid-December, General Phoumi then seized the capital, overthrew the Phouma Government, and installed Boun Oum as Prime Minister. In mid-1975, Pathet Lao troops moved towards the city and American personnel began evacuating the capital. On August 23, 1975, a contingent of 50 Pathet Lao women, symbolically "liberated" the city.[12] In December 2, 1975, the communist party of the Pathet Lao took over Vientiane and defeated the Kingdom of Laos which ended the Laotian Civil War, but the ongoing Insurgency in Laos began in the jungle, with the Pathet Lao fighting the Hmongs, Royalist-in-exile and the Right-wings.
In the 1950s and 1960s during the French-Indo China War and Vietnam War, thousands of refugees arrived in the province. By 1963, some 128,000 at arrived, especially Hmong people from Xiengkhouang Province.[13] Some 150,000 more arrived in the early 1970s.[13] Many of the refugees arrived were addicted to opium.[14] In 1989, the province was split into two parts, the Vientiane Prefecture, which contains the capital, Vientiane, and the remaining area, the Vientiane Province.
In late 2006, 13 ethnic Khmu Christians were arrested in the village of Khon Kean. One was released in April 2007, and on May 16, nine others were released after being held at a police detention facility in Hin Heup.[15] Vientiane hosted the 25th Southeast Asian Games in December 2009 celebrating the 50 years of SEA Games. The Xaysomboun region experiences sporadic violence between government forces and Hmong rebels.[16]
Geography
Vientiane Province, one of the provinces of Laos,[17] is a large province, covering an area of 15.927 kilômét vuông (6.149 dặm vuông Anh) with 10 districtsin mid north-western Laos. The province borders Luang Prabang Province to the north, Xiangkhouang Province to the northeast, Bolikhamxai Province to the east, Vientiane Prefecture and Thailand to the south, and Xaignabouli Province to the west. The principal towns are Vang Vieng and Muang Phôn-Hông. Vang Vieng is connected to Vientiane, roughly 170 kilômét (110 mi) by road to the south and Luang Prabang to the northwest by Route 13, the most important highway in the province, followed by Route 10.[18][19] Most of the population of the province is situated in the towns and villages along and near Route 13; from the south to the north these include Ban Phonsoung, Ban Saka and Toulakhom (along Route 10 east of Route 13), Ban Nalao, Ban Nong Khay, Ban Keng Kang, Ban Vang Khay, Ban Houay Pamon, Ban Namone, Vang Vieng, Ban Nampo, Ban Phatang, Ban Bome Phek, Ban Thieng, Muang Kasi and Ban Nam San Noi near the border with Xiangkhouang Province.[19]
Several kilometres to the south of Vang Vieng is one of Laos's largest lakes, Nam Ngum. Much of this area, particularly the forests of the southern part, are under the Phou Khao Khouay National Bio-Diversity Conservation Area.[19] To the east is the highest peak of Laos, Phou Bia, a heavily forested hilly area, east of Ban Thamkalong. The principal rivers flowing through the province are the Nam Song River, Nam Ngum River and the Nam Lik River.
-
Vang Vieng centre
-
Nam Song in Vang Vieng
-
Phu Phra mountain
-
Fish from the Nam Ngum
Protected areas
Phou Khao Khoay National Biodiversity Conservation Area is a protected area located 40 kilômét (25 mi) northeast of Vientiane. It was established on 29 October 1993 covering an area of 2,000 km2 extending into Khet Phiset Xaisomboon (Special Zone), Vientiane Prefecture and Vientiane Province. Its mountainous topography, with elevation varying from 200 m – 1761 m, emerged from "uplifting and exposure of the underlying sedimentary (Indosinias schist-clay-sandstone) complex". Sandstones are also seen spread in layers. extensive Flat uplands with sandstones with hardly any soil cover are also part of the topography of the park. It has a large stretch of mountain range with sandstone cliffs, river gorges and three large rivers with tributaries which flow into the Mekong River. It has monsoonal climate with recorded annual rainfall of 1936.1 mm (with higher reaches recording more rainfall). The mean annual temperature is 26.6 °C with recorded the mean maximum of 31.6 °C and the mean minimum temperature of 21.5 °C. The forests are evergreen, Shorea mixed deciduous forest, dry dipterocarp and pine type; particularly coniferous forest, of mono specific stands of Pinus merkusii, Fokienia hodgsonsii, bamboo (mai sanod), and fire-climax grasslands. Animals found here include elephants, tigers, bears, 13 pairs of white-cheeked gibbons, and langurs and many species of reptiles, amphibians and birds. The green peafowl has been reported here, near Ban Nakhay and Ban Nakhan Thoung, although it was generally considered to be extinct in Laos; conservation management has increased its population.[20][21]
Ban Na Reserve is a wildlife protected area where trekking is popular in its peripheral areas. The habitat is known for its bamboo, dense forest and wild elephants.[21][22]
The Mekong Channel upstream of Vientiane Important Bird Area (IBA) is 18,230 hectares in size. As its name implies it comprises an approximately 300 kilômét (190 mi) section of the Mekong Channel upstream of Vientiane city. It is situated in two provinces: Vientiane and Sainyabuli. The topography features braided streams, bushland, gravel bars, open sandy islands, rock outcrops, and sand bars. Notable avifauna include great thick-knees (Esacus recurvirostris), Jerdon's bushchat (Saxicola jerdoni), river lapwing (Vanellus duvaucelii), small pratincole (Glareola lactea), and wire-tailed swallow (Hirundo smithii).[23] Around the village of Ban Sivilay, a bird sanctuary has large flocks of whistling ducks and egrets roosting.[22]
Administrative divisions
The province is made up of the following 10 districts:[24]
Demographics
Population figures for the province increased dramatically during the period between 1943 (23,200) to 1955 (45,000). The demographics for ethnic breakdown in 1943 were: Lao 41.5%; Vietnamese (Annamites) 53%; Chinese 4%; Others 1.5%.[25] The population last reported was 388,833, as of March 2005 census with Muang Phôn-Hông as its capital.[26]
Economy
Since 2000, tourism in the region has rocketed, with many thousands visiting Vientiane and Vang Vieng every year. In recent years, new investment has gone into the suburbs of Vientiane. A tile factory has been established in the village of Phai Lom and a bio-organic fertilizer factory has been established in the village of Dong Xiengdy. Another tile factory has also been established in the village of Hathdeua, Keo Oudom District.[25] Lonely Planet said of the impact of tourism upon the town of Vang Vieng, "The growth of Vang Vieng has taken its toll. Inevitably the profile of the town has changed and the reason travelers first came here- to experience small-town Laos in a stunning setting – has been replaced by multistorey guesthouses. Even the local market has moved to a big, soulless slab of concrete north of the town.[27] In the “Ban Bo village of Thoulakhom District salt extraction is popular part time economic activity. The village is 60 kilometers from Vientiane and the extraction of salt is done by traditional methods.[22]
Although tourism has grown rapidly, most rural peoples still depend upon agriculture for their livelihoods. The Vientiane Plain which covers Vientiane Province and Vientiane Municipality is one of the six major rice producing plains in Laos.[28] Crafts and tailoring also employs a significant number, and most rural villages in the province have tailors who make pants, shirts, mosquito nets and sheets.[29] Herb doctors and carpenters are also occupations for a select few in the villages.[29] In the village of Ban Bo in Thoulakhom District is a salt extraction plant, employing most of the inhabitants in traditional extraction methods.[22]
Major operating companies in the mineral sector, as of 2008, include: Padeang Industry Public Co. Ltd, Phu Bin Ming Ltd, Laos Cement Co. Ltd, Wanrong Cement I, and Barite Mining Co.[30] As of 2009, each of the 126 ministry offices in Vientiane had IT facilities, including "one server, 10 PCs, a teleconference room, and a local area network connected to the national e-government infrastructure."[31]
Landmarks
There are numerous caves in the province, especially in the Vang Vieng area. Of note are the Patang, Patho Nokham, Vangxang and Tham Chang Caves. Vangxang Cave, also known as Elephant Court, contains the remains of an ancient sanctuary which preexisted the Lane Xang Kingdom, and contains five pink sandstone sculptures and two great Buddha images.[22] Vang Vieng contains several Buddhist temples dated to the 16th and 17th centuries; among them Wat Si Vieng Song (Wat That), Wat Kang and Wat Si Sum are of note.[32] Ecotourism is a significant contributor to the provincial economy, and Adventure Lao manages a kayaking operation on the Nam Song River, Nam Ngum River and the Nam Lik River, which enables tourists to pass many villages.[33] There is an artificial lake near the village of Ban Sivilay village with a protected bird habitat.[33] Also of note is Ban Ilai market in Muang Naxaithong, which sells basketry, pottery and other traditional crafts.[33]
Famous water falls seen in Phu Khao Khuay are Tat Xai (which has seven cascades), further downstream the Pha Xai (40 m fall) and Tat Luek.[34]
Wat Pha Bhat Phonson at Tha Pha Baht is a rocky formation where Buddha foot prints, reclining Buddha and a monastery with large ornamented stupa (built in 1933) are worshipped.[34]
Ban Pako village in the midst of thick forests, 55 km away from Vientiane has eco-lodges created over a 40 ha forest preserve, which is a tourist attraction. The houses in this village are made of bamboo thatch at an isolated location stated to have been a settlement 2000 years ago which has been attested by archaeological finds of artifacts. A wat and a water fall are also located here.[35]
The Nam Ngum Reservoir on the Nam Ngum River, within in the Nam Ngum Reserve is an important water resources project which extends over a water spread area of 1,280 hectares during the monsoon season.[21] The lake provides for recreational activities such as boating and picnics.[22] In the Ban Thalad village of Keo-Oudom District, about 80 kilômét (50 mi) from Vientiane, floating restaurants and sporting activities are popular.[22]
Among the many caves in the province, the Vangxang Cave also called the "Elephant Court" remnants of an ancient sanctuary of the Lane Xang Kingdom are seen. It is approachable along Route 13 (north) located at km 48, the cave has 5 large sculptures made of pink sandstone and also two massive images of Buddha.[22]
The Thoulakhom Zoo houses exotic and rare animals of Laos.[22]
-
Vang Xang
-
Tham Chang
-
Wat Si Vieng Song
-
Wat Kang
References
| Wikimedia Commons có thêm hình ảnh và phương tiện truyền tải về Viêng Chăn (tỉnh). |
- ^ a b c d “Vientiane Province History”. Lonely Planet. Truy cập ngày 30 tháng 11 năm 2012.
- ^ a b Fanthorpe 2009, tr. 66.
- ^ a b Võ 1972, tr. 21.
- ^ Askew, Logan & Long 2009, tr. 21.
- ^ a b c Grabowski 1995, tr. 111.
- ^ Askew, Logan & Long 2009, tr. 37.
- ^ Kislenko 2009, tr. 24.
- ^ Lee 2007, tr. 27.
- ^ Summary of World Broadcasts: Far East. Monitoring Service of the British Broadcasting Corporation. 1987. Truy cập ngày 30 tháng 11 năm 2012.
- ^ Doeden 2007, tr. 30.
- ^ Askew, Logan & Long 2009, tr. 77.
- ^ a b Eur 2002, tr. 736.
- ^ a b Jong & Donovan 2007, tr. 80.
- ^ Westermeyer 1983, tr. 203.
- ^ Államok 2007, tr. 865.
- ^ Martina, Michael (18 tháng 6 năm 2017). Birsel, Robert (biên tập). “China issues security alert in Laos after national shot dead”. Reuters.
Laos' Xaysomboun region has been plagued by sporadic conflict between the government and ethnic Hmong rebels for years.
- ^ “Home”. Regions. Official website of Laos Tourism. Truy cập ngày 7 tháng 1 năm 2013.
- ^ Lightner 2005, tr. 310.
- ^ a b c Maps (Bản đồ). Google Maps.
- ^ “Phou Khao Khouay”. Official Website of Ecotourism Organization. Truy cập ngày 10 tháng 12 năm 2012.
- ^ a b c “Phou Khao Khouay NBCA”. Official Website of Ecotourism Organization. Truy cập ngày 10 tháng 12 năm 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i “Vientiane Province”. Lao Tourism Organizataion. Truy cập ngày 30 tháng 11 năm 2012.
- ^ “Important Bird Areas factsheet: Mekong Channel upstream of Vientiane”. BirdLife International. 2012. Truy cập ngày 9 tháng 12 năm 2012.
- ^ “Destination: Vientiane Province”. Official website of Laos Tourism Organization. Truy cập ngày 10 tháng 12 năm 2012.
- ^ a b Askew, Logan & Long 2009, tr. 118.
- ^ “Provinces of Laos”. Statoids.com. Truy cập ngày 1 tháng 11 năm 2012.
- ^ Burke & Vaisutis 2007, tr. 122.
- ^ Bennett 2004, tr. 77.
- ^ a b Firth & Yamey 1964, tr. 93.
- ^ Geological Survey, 2010 & 14.
- ^ Akhtar, Hassan & Arinto 2009, tr. 244.
- ^ Burke & Vaisutis 2007, tr. 123.
- ^ a b c The Lao National Tourism Administration. “Vientiane Province”. Ecotourism Laos. GMS Sustainable Tourism Development Project in Lao PDR. Truy cập ngày 1 tháng 12 năm 2012.
- ^ a b Burke 2007, tr. 119.
- ^ Burke 2007, tr. 116–117.
Bibliography
- Akhtar, Shahid; Arinto, Patricia B.; Abu, Hassan, Musa (3 tháng 6 năm 2009). Digital Review of Asia Pacific 2009–2010. IDRC. ISBN 978-81-321-0084-3.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Államok, Egyesült. Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2007. Government Printing Office. tr. 865.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Askew, Marc; Logan, Williams S.; Long, Colin (2009). Vientiane: Transformation of a Lao landscape. Routledge. tr. 118–. ISBN 978-1-134-32365-4.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Bennett, J. (1 tháng 1 năm 2004). New Approaches to Gall Midge Resistance in Rice. Int. Rice Res. Inst. ISBN 978-971-22-0198-1.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Burke, Andrew; Vaisutis, Justine (1 tháng 8 năm 2007). Laos 6th Edition. Lonely Planet. ISBN 978-1-74104-568-0.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Doeden, Matt (1 tháng 1 năm 2007). Laos in Pictures. Twenty-First Century Books. ISBN 978-0-8225-6590-1.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Eur (2002). Far East and Australasia 2003. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-1-85743-133-9.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Fanthorpe, Lionel & Patricia (23 tháng 3 năm 2009). Secrets of the World's Undiscovered Treasures. Dundurn. ISBN 978-1-77070-384-1.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Firth, Raymond; Yamey, Basil S. (1964). Capital, Saving & Credit in Peasant Societies. Transaction Publishers. ISBN 978-0-202-30918-7.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Geological Survey (U S ) (25 tháng 10 năm 2010). Minerals Yearbook: Area Reports: International 2008: Asia and the Pacific. Government Printing Office. tr. 14–. ISBN 978-1-4113-2964-5.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Grabowsky, Volker (1995). Regions and National Integration in Thailand, 1892–1992. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. ISBN 978-3-447-03608-5.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Jong, Wil De; Donovan, Deanna; Ken-ichi Abe (5 tháng 3 năm 2007). Extreme Conflict and Tropical Forests. Springer. ISBN 978-1-4020-5461-7.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Kislenko, Arne (2009). Culture And Customs Of Laos. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-0-313-33977-6.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Lee, Jonathan H. X. (17 tháng 9 năm 2012). Laotians in the San Francisco Bay Area. The Center for Lao Studies, Arcadia Publishing. ISBN 978-0-7385-9586-3.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Lightner, Jr, Sam (30 tháng 10 năm 2005). Thailand: A Climbing Guide. The Mountaineers Books. ISBN 978-0-89886-750-3.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Võ, Thu Tịnh (1972). The Phra Lak-Phra Lam (The Lao version of the Ramayana).: Abridged translation of the manuscript of Vat Kang Tha. Cultural Survey of Laos.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)
- Westermeyer, Joseph (1983). Poppies, Pipes, and People: Opium and Its Use in Laos. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-04622-1.Quản lý CS1: ref=harv (liên kết)