Khác biệt giữa bản sửa đổi của “Acid glyoxylic”
nKhông có tóm lược sửa đổi Thẻ: Đã bị lùi lại Xóa từ 50% đến 90% nội dung Xóa bản mẫu Chất lượng kém Soạn thảo trực quan Sửa đổi di động Sửa đổi từ trang di động Sửa đổi di động nâng cao |
nKhông có tóm lược sửa đổi Thẻ: Đã bị lùi lại Soạn thảo trực quan Sửa đổi di động Sửa đổi từ trang di động Sửa đổi di động nâng cao |
||
| Dòng 36: | Dòng 36: | ||
}}}} |
}}}} |
||
'''Axit glyoxylic''' hoặc '''axit oxoacetic ''' là một [[hợp chất hữu cơ]]. Cùng với [[axit axetic]], [[axit glycolic]] và [[axit oxalic]], axit glyoxylic là một trong C<sub>2 </sub> [[Axit cacboxylic | axit cacboxylic]]. Nó là một chất rắn không màu xuất hiện tự nhiên và hữu ích trong công nghiệp. |
'''Axit glyoxylic''' hoặc '''axit oxoacetic ''' là một [[hợp chất hữu cơ]]. Cùng với [[axit axetic]], [[axit glycolic]] và [[axit oxalic]], axit glyoxylic là một trong C<sub>2 </sub> [[Axit cacboxylic | axit cacboxylic]]. Nó là một chất rắn không màu xuất hiện tự nhiên và hữu ích trong công nghiệp. |
||
== Cấu trúc và danh pháp == |
|||
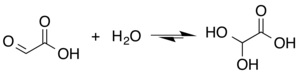
Mặc dù cấu trúc của axit glyoxylic được mô tả là có [[Nhóm chức|nhóm chưc]] [[andehit]] , andehit chỉ là một thành phần phụ của dạng phổ biến nhất trong một số trường hợp. Thay vào đó, nó thường tồn tại dưới dạng hyđrat hoặc chu kỳ [[Dimer (chemistry)|dimer]]. Ví dụ, khi có nước, [[Cacbonyl|carbonyl]] nhanh chóng chuyển đổi thành một [[Geminal diol|diol đá quý]] (được mô tả là "monohydrat"). [[Hằng số cân bằng]] (''K'') là 300 đối với sự hình thành axit dihydroxyacetic ở nhiệt độ phòng:<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Sørensen|first1=P. E.|last2=Bruhn|first2=K.|last3=Lindeløv|first3=F.|year=1974|title=Kinetics and equilibria for the reversible hydration of the aldehyde group in glyoxylic acid.|journal=Acta Chem. Scand.|volume=28|pages=162–168|doi=10.3891/acta.chem.scand.28a-0162|doi-access=free}}</ref> |
|||
: [[Tập_tin:Glyoxylic_acid_hydration.png|300x300px]] |
|||
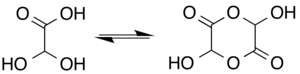
Trong dung dịch, monohydrat tồn tại ở trạng thái cân bằng với [[hemiacetal]] dạng dimer :<ref name="Ull">Georges Mattioda and Yani Christidis “Glyoxylic Acid” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. {{DOI|10.1002/14356007.a12_495}}</ref> |
|||
: [[Tập_tin:Glyoxylic_acid_hydrate_dimerization.png|300x300px]] |
|||
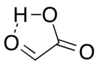
Trong sự cô lập, cấu trúc anđehit có vai trò là một [[đồng đẳng]] chính là [[cấu trúc liên kết hiđro]] mạch vòng với anđehit cacbonyl gần với hiđro [[cacboxyl]]:<ref>{{cite journal|last1=Redington|first1=Richard L.|last2=Liang|first2=Chin-Kang Jim|year=1984|title=Vibrational spectra of glyoxylic acid monomers|journal=Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy|volume=104|issue=1|pages=25–39|bibcode=1984JMoSp.104...25R|doi=10.1016/0022-2852(84)90242-X}}</ref> |
|||
: [[Tập_tin:Glyoxylic_acid_H-bonded.png|100x100px]] |
|||
Hằng số [[Henry's law|định luật Henry]] của axit glyoxylic là K<sub>H</sub> = 1.09 × 10<sup>4</sup> × exp[(40.0 × 10<sup>3</sup>/R) × (1/T − 1/298)].<ref>{{cite journal|last=Ip|first=H. S. Simon|author2=Huang, X. H. Hilda|author3=Yu, Jian Zhen|year=2009|title=Effective Henry's law constants of glyoxal, glyoxylic acid, and glycolic acid|url=http://repository.ust.hk/ir/bitstream/1783.1-6115/1/HLCpaper2ndrevision.pdf|journal=Geophysical Research Letters|volume=36|issue=1|pages=L01802|bibcode=2009GeoRL..36.1802I|doi=10.1029/2008GL036212}}</ref> |
|||
== Điều chế == |
|||
[[Conjugate base|Cơ sơ liên hợp]] của axit glyoxylic được gọi là glyoxylate và là dạng hợp chất tồn tại trong dung dịch ở pH trung tính. Glyoxylate là sản phẩm phụ của [[Amidation|amid hóa]] quá trình sinh tổng hợp một số [[Peptide|peptides]] amid hóa. |
|||
Đối với hồ sơ lịch sử, axit glyoxylic được điều chế từ axit oxalic bằng [[phương phap điện tổng hợp]]:<ref>{{cite journal|author1=Tafel, Julius|author2=Friedrichs, Gustav|year=1904|title=Elektrolytische Reduction von Carbonsäuren und Carbonsäureestern in schwefelsaurer Lösung|url=https://zenodo.org/record/1426114|journal=Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft|volume=37|issue=3|pages=3187–3191|doi=10.1002/cber.190403703116}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=http://www.sciencemadness.org/library/books/practical_organic_chemistry.pdf|title=Practical Organic Chemistry 2nd Ed.|last=Cohen|first=Julius|publisher=Macmillan and Co. Limited|year=1920|location=London|pages=102–104}}</ref> trong tổng hợp hữu cơ, cực âm [[chì dioxit]] đã được áp dụng để điều chế axit glyoxylic từ [[Oxalic acid|axit oxalic]] trong chất điện phân axit sulfuric.<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ArsfQZig_9AC&pg=PA573|title=Materials Handbook: A Concise Desktop Reference|author=François Cardarelli|publisher=Springer|year=2008|isbn=978-1-84628-668-1|page=574}}</ref> |
|||
: [[Tập_tin:GlyoxalicAcidElectrosyn.png|380x380px]] |
|||
[[Axit nitric]] nóng có thể [[oxy hóa hữu cơ]] glyoxan thành glyoxylic; tuy nhiên phản ứng này tỏa nhiệt cao và dễ xảy ra hiện tượng thoát nhiệt. Ngoài ra, axit oxalic là sản phẩm phụ chính. |
|||
Ngoài ra, quá trình [[ozo hóa]] [[axit maleic]] cũng có hiệu quả.<ref name="Ull" /> |
|||
== Vai trò sinh học == |
|||
Glyoxylate là chất trung gian của [[Glyoxylate cycle|chu kì glyoxylat]], điều này [[sinh vật]], chẳng hạn như vi khuẩn,<ref name="Holms">{{cite journal|author=Holms WH|year=1987|title=Control of flux through the citric acid cycle and the glyoxylate bypass in Escherichia coli|journal=Biochem Soc Symp.|volume=54|pages=17–31|pmid=3332993}}</ref> nấm và thực vật <ref name="Escher and Widmer F">{{cite journal|vauthors=Escher CL, Widmer F|year=1997|title=Lipid mobilization and gluconeogenesis in plants: do glyoxylate cycle enzyme activities constitute a real cycle? A hypothesis|journal=Biol. Chem.|volume=378|issue=8|pages=803–813|pmid=9377475}}</ref> chuyển đổi [[axit béo]] thành [[Carbohydrate|carbohydrat]]. Chu trình glyoxylate cũng rất quan trọng đối với việc cảm ứng các cơ chế bảo vệ thực vật để phản ứng với nấm.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Dubey|first1=Mukesh K.|last2=Broberg|first2=Anders|last3=Sooriyaarachchi|first3=Sanjeewani|last4=Ubhayasekera|first4=Wimal|last5=Jensen|first5=Dan Funck|last6=Karlsson|first6=Magnus|date=September 2013|title=The glyoxylate cycle is involved in pleotropic phenotypes, antagonism and induction of plant defence responses in the fungal biocontrol agent Trichoderma atroviride|journal=Fungal Genetics and Biology|volume=58–59|pages=33–41|doi=10.1016/j.fgb.2013.06.008|issn=1087-1845|pmid=23850601}}</ref> Chu trình glyoxylate được bắt đầu thông qua hoạt động của isocitrate lyase, chuyển isocitrate thành glyoxylate và succinate. Nghiên cứu đang được thực hiện để đồng chọn con đường cho nhiều mục đích sử dụng khác nhau như sinh tổng hợp succinate.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Zhu|first1=Li-Wen|last2=Li|first2=Xiao-Hong|last3=Zhang|first3=Lei|last4=Li|first4=Hong-Mei|last5=Liu|first5=Jian-Hua|last6=Yuan|first6=Zhan-Peng|last7=Chen|first7=Tao|last8=Tang|first8=Ya-Jie|date=November 2013|title=Activation of glyoxylate pathway without the activation of its related gene in succinate-producing engineered Escherichia coli|journal=Metabolic Engineering|volume=20|pages=9–19|doi=10.1016/j.ymben.2013.07.004|issn=1096-7176|pmid=23876414}}</ref> |
|||
=== Ở người === |
|||
Glyoxylate được sản xuất thông qua hai con đường: thông qua quá trình oxy hóa glycolat trong peroxisome hoặc thông qua quá trình dị hóa hydroxyproline trong ti thể.<ref name=":0">{{Cite journal|last1=Belostotsky|first1=Ruth|last2=Pitt|first2=James Jonathon|last3=Frishberg|first3=Yaacov|date=2012-12-01|title=Primary hyperoxaluria type III—a model for studying perturbations in glyoxylate metabolism|journal=Journal of Molecular Medicine|volume=90|issue=12|pages=1497–1504|doi=10.1007/s00109-012-0930-z|issn=0946-2716|pmid=22729392|hdl-access=free|hdl=11343/220107|s2cid=11549218}}</ref> Trong peroxisomes, glyoxylate được chuyển đổi thành glycine bởi AGT1 hoặc thành oxalate bởi glycolat oxidase. Trong ty thể, glyoxylate được AGT2 chuyển thành glycine hoặc thành glycolat nhờ glycolat reductase. Một lượng nhỏ glyoxylate được chuyển hóa thành oxalate bởi lactate dehydrogenase trong tế bào chất.<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal|last1=Schnedler|first1=Nina|last2=Burckhardt|first2=Gerhard|last3=Burckhardt|first3=Birgitta C.|date=March 2011|title=Glyoxylate is a substrate of the sulfate-oxalate exchanger, sat-1, and increases its expression in HepG2 cells|journal=Journal of Hepatology|volume=54|issue=3|pages=513–520|doi=10.1016/j.jhep.2010.07.036|issn=0168-8278|pmid=21093948}}</ref> |
|||
[[Tập_tin:Glyoxylate_metabolism_in_hepatocytes.jpg|giữa|nhỏ|600x600px|Chuyển hóa oxalat và glyoxylat trong tế bào gan. AGT1 và 2, alanin: glyoxylate aminotransferase 1 và 2; ĐI, glycolat oxidase; GR, glyoxylate reductase; HKGA, 4-hydroxy-2-ketoglutarate lyase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase]] |
|||
=== Trong thực vật === |
|||
Ngoài vai trò là chất trung gian trong con đường glyoxylate, glyoxylate cũng là chất trung gian quan trọng trong con đường [[quang hợp]] . Quang hợp là kết quả của phản ứng phụ của RuBisCO với O2 thay vì CO2. Mặc dù lúc đầu được coi là lãng phí năng lượng và tài nguyên, quang hợp đã được chứng minh là một phương pháp quan trọng để tái tạo carbon và CO2, loại bỏ phosphoglycolat độc hại và khởi động cơ chế bảo vệ.<ref>{{Cite web|url=http://www2.mcdaniel.edu/Biology/botf99/photodark/photorespiration.htm|title=photorespiration|access-date=2017-03-09}}</ref><ref name=":2">{{Cite journal|last1=Peterhansel|first1=Christoph|last2=Horst|first2=Ina|last3=Niessen|first3=Markus|last4=Blume|first4=Christian|last5=Kebeish|first5=Rashad|last6=Kürkcüoglu|first6=Sophia|last7=Kreuzaler|first7=Fritz|date=2010-03-23|title=Photorespiration|journal=The Arabidopsis Book / American Society of Plant Biologists|volume=8|page=e0130|doi=10.1199/tab.0130|issn=1543-8120|pmc=3244903|pmid=22303256}}</ref> Trong phản ứng quang hợp, glyoxylate được chuyển đổi từ glycolat thông qua hoạt động của glycolat oxidase trong peroxisome. Sau đó, nó được chuyển đổi thành glycine thông qua các hoạt động song song của SGAT và GGAT, sau đó được vận chuyển vào ty thể.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Zhang|first1=Zhisheng|last2=Mao|first2=Xingxue|last3=Ou|first3=Juanying|last4=Ye|first4=Nenghui|last5=Zhang|first5=Jianhua|last6=Peng|first6=Xinxiang|date=January 2015|title=Distinct photorespiratory reactions are preferentially catalyzed by glutamate:glyoxylate and serine:glyoxylate aminotransferases in rice|journal=Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology|volume=142|pages=110–117|doi=10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.11.009|issn=1011-1344|pmid=25528301}}</ref><ref name=":2" /> It has also been reported that the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex may play a role in glycolate and glyoxylate metabolism.<ref>{{Cite journal|last1=Blume|first1=Christian|last2=Behrens|first2=Christof|last3=Eubel|first3=Holger|last4=Braun|first4=Hans-Peter|last5=Peterhansel|first5=Christoph|date=November 2013|title=A possible role for the chloroplast pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in plant glycolate and glyoxylate metabolism|journal=Phytochemistry|volume=95|pages=168–176|doi=10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.07.009|issn=0031-9422|pmid=23916564}}</ref> |
|||
[[Tập_tin:Photorespiration_in_arabidopsis.jpg|giữa|nhỏ|600x600px|Basic overview of photorespiration in Arabidopsis. GGAT, glyoxylate:glutamate aminotransferase; GLYK, glycerate kinase; GO, glycolate oxidase; HPR, hydroxypyruvate reductase; PGLP, phosphoglycolate phosphatase; Rubisco, RuBP carboxylase/oxygenase; SGAT, serine:glyoxylate aminotransferase; SHM, serine hydroxymethyltransferase]] |
|||
Phiên bản lúc 00:00, ngày 26 tháng 2 năm 2021
| Glyoxylic acid | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Tên hệ thống | Axit oxoethanoic |
| Tên khác | Axit glyoxylic [1] 2-Axit oxoacetic Axit formylformic |
| Nhận dạng | |
| Số CAS | |
| PubChem | |
| DrugBank | DB04343 |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Ảnh Jmol-3D | ảnh |
| SMILES | đầy đủ
|
| InChI | đầy đủ
|
| UNII | |
| Thuộc tính | |
| Khối lượng riêng | 1.384 g/mL |
| Điểm nóng chảy | 80 °C (353 K; 176 °F)[2] |
| Điểm sôi | 111 °C (384 K; 232 °F) |
| Độ axit (pKa) | 3.18,[3] 3.32 [4] |
| Các hợp chất liên quan | |
| Anion khác | glyoxylat |
| Nhóm chức liên quan | axit formic axit acetic axit glycolic axit oxalic axit propionic axit pyruvic |
| Hợp chất liên quan | acetandehit glyoxan glycolandehit |
Trừ khi có ghi chú khác, dữ liệu được cung cấp cho các vật liệu trong trạng thái tiêu chuẩn của chúng (ở 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Axit glyoxylic hoặc axit oxoacetic là một hợp chất hữu cơ. Cùng với axit axetic, axit glycolic và axit oxalic, axit glyoxylic là một trong C2 axit cacboxylic. Nó là một chất rắn không màu xuất hiện tự nhiên và hữu ích trong công nghiệp.
Cấu trúc và danh pháp
Mặc dù cấu trúc của axit glyoxylic được mô tả là có nhóm chưc andehit , andehit chỉ là một thành phần phụ của dạng phổ biến nhất trong một số trường hợp. Thay vào đó, nó thường tồn tại dưới dạng hyđrat hoặc chu kỳ dimer. Ví dụ, khi có nước, carbonyl nhanh chóng chuyển đổi thành một diol đá quý (được mô tả là "monohydrat"). Hằng số cân bằng (K) là 300 đối với sự hình thành axit dihydroxyacetic ở nhiệt độ phòng:[5]
Trong dung dịch, monohydrat tồn tại ở trạng thái cân bằng với hemiacetal dạng dimer :[6]
Trong sự cô lập, cấu trúc anđehit có vai trò là một đồng đẳng chính là cấu trúc liên kết hiđro mạch vòng với anđehit cacbonyl gần với hiđro cacboxyl:[7]
Hằng số định luật Henry của axit glyoxylic là KH = 1.09 × 104 × exp[(40.0 × 103/R) × (1/T − 1/298)].[8]
Điều chế
Cơ sơ liên hợp của axit glyoxylic được gọi là glyoxylate và là dạng hợp chất tồn tại trong dung dịch ở pH trung tính. Glyoxylate là sản phẩm phụ của amid hóa quá trình sinh tổng hợp một số peptides amid hóa.
Đối với hồ sơ lịch sử, axit glyoxylic được điều chế từ axit oxalic bằng phương phap điện tổng hợp:[9][10] trong tổng hợp hữu cơ, cực âm chì dioxit đã được áp dụng để điều chế axit glyoxylic từ axit oxalic trong chất điện phân axit sulfuric.[11]
Axit nitric nóng có thể oxy hóa hữu cơ glyoxan thành glyoxylic; tuy nhiên phản ứng này tỏa nhiệt cao và dễ xảy ra hiện tượng thoát nhiệt. Ngoài ra, axit oxalic là sản phẩm phụ chính.
Ngoài ra, quá trình ozo hóa axit maleic cũng có hiệu quả.[6]
Vai trò sinh học
Glyoxylate là chất trung gian của chu kì glyoxylat, điều này sinh vật, chẳng hạn như vi khuẩn,[12] nấm và thực vật [13] chuyển đổi axit béo thành carbohydrat. Chu trình glyoxylate cũng rất quan trọng đối với việc cảm ứng các cơ chế bảo vệ thực vật để phản ứng với nấm.[14] Chu trình glyoxylate được bắt đầu thông qua hoạt động của isocitrate lyase, chuyển isocitrate thành glyoxylate và succinate. Nghiên cứu đang được thực hiện để đồng chọn con đường cho nhiều mục đích sử dụng khác nhau như sinh tổng hợp succinate.[15]
Ở người
Glyoxylate được sản xuất thông qua hai con đường: thông qua quá trình oxy hóa glycolat trong peroxisome hoặc thông qua quá trình dị hóa hydroxyproline trong ti thể.[16] Trong peroxisomes, glyoxylate được chuyển đổi thành glycine bởi AGT1 hoặc thành oxalate bởi glycolat oxidase. Trong ty thể, glyoxylate được AGT2 chuyển thành glycine hoặc thành glycolat nhờ glycolat reductase. Một lượng nhỏ glyoxylate được chuyển hóa thành oxalate bởi lactate dehydrogenase trong tế bào chất.[17]

Trong thực vật
Ngoài vai trò là chất trung gian trong con đường glyoxylate, glyoxylate cũng là chất trung gian quan trọng trong con đường quang hợp . Quang hợp là kết quả của phản ứng phụ của RuBisCO với O2 thay vì CO2. Mặc dù lúc đầu được coi là lãng phí năng lượng và tài nguyên, quang hợp đã được chứng minh là một phương pháp quan trọng để tái tạo carbon và CO2, loại bỏ phosphoglycolat độc hại và khởi động cơ chế bảo vệ.[18][19] Trong phản ứng quang hợp, glyoxylate được chuyển đổi từ glycolat thông qua hoạt động của glycolat oxidase trong peroxisome. Sau đó, nó được chuyển đổi thành glycine thông qua các hoạt động song song của SGAT và GGAT, sau đó được vận chuyển vào ty thể.[20][19] It has also been reported that the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex may play a role in glycolate and glyoxylate metabolism.[21]

- ^ Lỗi chú thích: Thẻ
<ref>sai; không có nội dung trong thẻ ref có têniupac2013 - ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 4394
- ^ Dissociation Constants Of Organic Acids and Bases (600 compounds), http://zirchrom.com/organic.htm.
- ^ pKa Data Compiled by R. Williams, “Archived copy” (PDF). Bản gốc (PDF) lưu trữ ngày 2 tháng 6 năm 2010. Truy cập ngày 2 tháng 6 năm 2010.Quản lý CS1: bản lưu trữ là tiêu đề (liên kết).
- ^ Sørensen, P. E.; Bruhn, K.; Lindeløv, F. (1974). “Kinetics and equilibria for the reversible hydration of the aldehyde group in glyoxylic acid”. Acta Chem. Scand. 28: 162–168. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.28a-0162.
- ^ a b Georges Mattioda and Yani Christidis “Glyoxylic Acid” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a12_495
- ^ Redington, Richard L.; Liang, Chin-Kang Jim (1984). “Vibrational spectra of glyoxylic acid monomers”. Journal of Molecular Spectroscopy. 104 (1): 25–39. Bibcode:1984JMoSp.104...25R. doi:10.1016/0022-2852(84)90242-X.
- ^ Ip, H. S. Simon; Huang, X. H. Hilda; Yu, Jian Zhen (2009). “Effective Henry's law constants of glyoxal, glyoxylic acid, and glycolic acid” (PDF). Geophysical Research Letters. 36 (1): L01802. Bibcode:2009GeoRL..36.1802I. doi:10.1029/2008GL036212.
- ^ Tafel, Julius; Friedrichs, Gustav (1904). “Elektrolytische Reduction von Carbonsäuren und Carbonsäureestern in schwefelsaurer Lösung”. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 37 (3): 3187–3191. doi:10.1002/cber.190403703116.
- ^ Cohen, Julius (1920). Practical Organic Chemistry 2nd Ed (PDF). London: Macmillan and Co. Limited. tr. 102–104.
- ^ François Cardarelli (2008). Materials Handbook: A Concise Desktop Reference. Springer. tr. 574. ISBN 978-1-84628-668-1.
- ^ Holms WH (1987). “Control of flux through the citric acid cycle and the glyoxylate bypass in Escherichia coli”. Biochem Soc Symp. 54: 17–31. PMID 3332993.
- ^ Escher CL, Widmer F (1997). “Lipid mobilization and gluconeogenesis in plants: do glyoxylate cycle enzyme activities constitute a real cycle? A hypothesis”. Biol. Chem. 378 (8): 803–813. PMID 9377475.
- ^ Dubey, Mukesh K.; Broberg, Anders; Sooriyaarachchi, Sanjeewani; Ubhayasekera, Wimal; Jensen, Dan Funck; Karlsson, Magnus (tháng 9 năm 2013). “The glyoxylate cycle is involved in pleotropic phenotypes, antagonism and induction of plant defence responses in the fungal biocontrol agent Trichoderma atroviride”. Fungal Genetics and Biology. 58–59: 33–41. doi:10.1016/j.fgb.2013.06.008. ISSN 1087-1845. PMID 23850601.
- ^ Zhu, Li-Wen; Li, Xiao-Hong; Zhang, Lei; Li, Hong-Mei; Liu, Jian-Hua; Yuan, Zhan-Peng; Chen, Tao; Tang, Ya-Jie (tháng 11 năm 2013). “Activation of glyoxylate pathway without the activation of its related gene in succinate-producing engineered Escherichia coli”. Metabolic Engineering. 20: 9–19. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2013.07.004. ISSN 1096-7176. PMID 23876414.
- ^ Belostotsky, Ruth; Pitt, James Jonathon; Frishberg, Yaacov (1 tháng 12 năm 2012). “Primary hyperoxaluria type III—a model for studying perturbations in glyoxylate metabolism”. Journal of Molecular Medicine. 90 (12): 1497–1504. doi:10.1007/s00109-012-0930-z. hdl:11343/220107. ISSN 0946-2716. PMID 22729392. S2CID 11549218.
- ^ Schnedler, Nina; Burckhardt, Gerhard; Burckhardt, Birgitta C. (tháng 3 năm 2011). “Glyoxylate is a substrate of the sulfate-oxalate exchanger, sat-1, and increases its expression in HepG2 cells”. Journal of Hepatology. 54 (3): 513–520. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2010.07.036. ISSN 0168-8278. PMID 21093948.
- ^ “photorespiration”. Truy cập ngày 9 tháng 3 năm 2017.
- ^ a b Peterhansel, Christoph; Horst, Ina; Niessen, Markus; Blume, Christian; Kebeish, Rashad; Kürkcüoglu, Sophia; Kreuzaler, Fritz (23 tháng 3 năm 2010). “Photorespiration”. The Arabidopsis Book / American Society of Plant Biologists. 8: e0130. doi:10.1199/tab.0130. ISSN 1543-8120. PMC 3244903. PMID 22303256.
- ^ Zhang, Zhisheng; Mao, Xingxue; Ou, Juanying; Ye, Nenghui; Zhang, Jianhua; Peng, Xinxiang (tháng 1 năm 2015). “Distinct photorespiratory reactions are preferentially catalyzed by glutamate:glyoxylate and serine:glyoxylate aminotransferases in rice”. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology. 142: 110–117. doi:10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2014.11.009. ISSN 1011-1344. PMID 25528301.
- ^ Blume, Christian; Behrens, Christof; Eubel, Holger; Braun, Hans-Peter; Peterhansel, Christoph (tháng 11 năm 2013). “A possible role for the chloroplast pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in plant glycolate and glyoxylate metabolism”. Phytochemistry. 95: 168–176. doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.07.009. ISSN 0031-9422. PMID 23916564.