Tegafur
 | |
 | |
| Dữ liệu lâm sàng | |
|---|---|
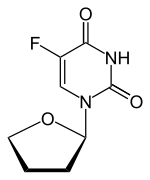
| Đồng nghĩa | 5-fluoro-1-(oxolan-2-yl)pyrimidine-2,4-dione |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Tên thuốc quốc tế |
| Giấy phép | |
| Danh mục cho thai kỳ |
|
| Dược đồ sử dụng | Oral |
| Mã ATC | |
| Tình trạng pháp lý | |
| Tình trạng pháp lý | |
| Dữ liệu dược động học | |
| Chu kỳ bán rã sinh học | 3.9-11 hours |
| Các định danh | |
Tên IUPAC
| |
| Số đăng ký CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Định danh thành phần duy nhất | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.027 |
| Dữ liệu hóa lý | |
| Công thức hóa học | C8H9FN2O3 |
| Khối lượng phân tử | 200.16 g/mol |
| Mẫu 3D (Jmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Định danh hóa học quốc tế
| |
| (kiểm chứng) | |
Tegafur là một tiền chất hóa trị liệu của 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) được sử dụng trong điều trị ung thư. Nó là một thành phần của thuốc kết hợp tegafur/uracil. Khi được chuyển hóa, nó trở thành 5-FU.[1]
Nó đã được cấp bằng sáng chế vào năm 1967 và được chấp thuận cho sử dụng y tế vào năm 1972.[2]
Sử dụng trong y tế
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Là một tiền chất của 5-FU, nó được sử dụng trong điều trị các bệnh ung thư sau:[3]
- Dạ dày (khi kết hợp với gimeracil và oteracil)
- Vú (với uracil)
- Túi mật
- Phổi (cụ thể là ung thư biểu mô tuyến, điển hình là với uracil)
- Trực tràng (thường khi kết hợp với gimeracil và oteracil)
- Đầu và cổ
- Gan (với uracil) [4]
- Tụy
Nó thường được dùng kết hợp với các loại thuốc làm thay đổi tính khả dụng sinh học và độc tính của nó như gimeracil, oteracil hoặc uracil.[3] Các tác nhân này đạt được điều này bằng cách ức chế enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (uracil/gimeracil) hoặc orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (oteracil).[3]
Tác dụng phụ
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Các tác dụng phụ chính của tegafur tương tự như fluorouracil và bao gồm ức chế tủy, nhiễm độc thần kinh trung ương và nhiễm độc đường tiêu hóa (đặc biệt là tiêu chảy).[3] Nhiễm độc đường tiêu hóa là tác dụng phụ giới hạn liều của tegafur.[3] Nhiễm độc thần kinh trung ương phổ biến hơn với tegafur so với fluorouracil.[3]
Dược động học
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD) chịu trách nhiệm giải độc chuyển hóa fluoropyrimidine, một nhóm thuốc bao gồm 5-fluorouracil, capecitabine và tegafur.[5] Các biến thể di truyền trong gen DPD (DPYD) có thể dẫn đến giảm hoặc không có hoạt động DPD, và các cá nhân dị hợp tử hoặc đồng hợp tử cho các biến thể này có thể bị thiếu DPD một phần hoặc hoàn toàn; ước tính 0,2% cá nhân bị thiếu DPD hoàn toàn.[5][6] Những người bị thiếu hụt DPD một phần hoặc toàn bộ có nguy cơ tăng độc tính nghiêm trọng hoặc thậm chí gây tử vong khi điều trị bằng fluoropyrimidine; ví dụ về độc tính bao gồm ức chế tủy, nhiễm độc thần kinh và hội chứng chân tay.[5][6]
Cơ chế hoạt động
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Nó là một tiền chất của 5-FU, là một chất ức chế tổng hợp thymidylate.[3]
Dược động học
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Nó được chuyển hóa thành 5-FU bởi CYP2A6.[7][8]
Bản đồ đường dẫn tương tác
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Bản mẫu:FluoropyrimidineActivity WP1601
Xem thêm
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Tham khảo
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]- ^ El Sayed, YM; Sadée, W (1983). “Metabolic activation of R,S-1-(tetrahydro-2-furanyl)-5-fluorouracil (ftorafur) to 5-fluorouracil by soluble enzymes”. Cancer Research. 43 (9): 4039–44. PMID 6409396.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery (bằng tiếng Anh). John Wiley & Sons. tr. 511. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ a b c d e f g Sweetman, S biên tập (ngày 14 tháng 11 năm 2011). “Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference”. Pharmaceutical Press. Truy cập ngày 12 tháng 2 năm 2014.
- ^ Ishikawa, T (ngày 14 tháng 5 năm 2008). “Chemotherapy with enteric-coated tegafur/uracil for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma”. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 14 (18): 2797–2801. doi:10.3748/wjg.14.2797. PMC 2710718. PMID 18473401.
- ^ a b c Caudle, KE; Thorn, CF; Klein, TE; Swen, JJ; McLeod, HL; Diasio, RB; Schwab, M (tháng 12 năm 2013). “Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium guidelines for dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase genotype and fluoropyrimidine dosing”. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 94 (6): 640–5. doi:10.1038/clpt.2013.172. PMC 3831181. PMID 23988873.
- ^ a b Amstutz, U; Froehlich, TK; Largiadèr, CR (tháng 9 năm 2011). “Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase gene as a major predictor of severe 5-fluorouracil toxicity”. Pharmacogenomics. 12 (9): 1321–36. doi:10.2217/pgs.11.72. PMID 21919607.
- ^ Nakayama, T; Noguchi, S (tháng 1 năm 2010). “Therapeutic usefulness of postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with Tegafur-Uracil (UFT) in patients with breast cancer: focus on the results of clinical studies in Japan”. The Oncologist. 15 (1): 26–36. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0255. PMC 3227888. PMID 20080863.
- ^ Matt P, van Zwieten-Boot B, Calvo Rojas G, Ter Hofstede H, Garcia-Carbonero R, Camarero J, Abadie E, Pignatti F (tháng 10 năm 2011). “The European Medicines Agency review of Tegafur/Gimeracil/Oteracil (Teysuno™) for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer when given in combination with cisplatin: summary of the Scientific Assessment of the Committee for medicinal products for human use (CHMP)”. The Oncologist. 16 (10): 1451–1457. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2011-0224. PMC 3228070. PMID 21963999.

