Khác biệt giữa bản sửa đổi của “Thẩm phân máu”
←Tẩy trống trang |
n Đã lùi lại sửa đổi của EverlastingRoad (Thảo luận) quay về phiên bản cuối của Alphama |
||
| Dòng 1: | Dòng 1: | ||
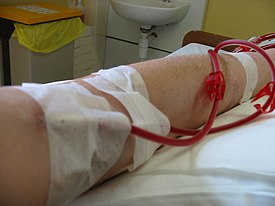
[[File:Plugged into dialysis.jpg|right|thumb|275px|Quá trình thẩm phân máu]] |
|||
[[Image:Hemodialysismachine.jpg|250px|right|thumb|Máy lọc máu]] |
|||
{{Đang dịch 2 (nguồn)|ngày=26 |
|||
|tháng=12 |
|||
|năm=2013 |
|||
|1 = |
|||
}} |
|||
Trong y học, '''Thẩm phân máu''' ('''haemodialysis''' hay '''haemodialysis''') là phương pháp loại bỏ các chất thải như [[creatinine]], [[urea]], nước tự do từ máu được thực hiện bên ngoài cơ thể ở bệnh nhân [[suy thận]]. Thẩm phân máu là một trong ba [[phương pháp thay thế thận]] (hai phương pháp khác là [[phẩu thuật thay thận]] và [[thẩm phân phuc mạc]]). Phương pháp thay thế for extracorporeal separation of thành phần máu như huyết tương hoặc tế bào is [[apheresis]]. |
|||
Thẩm phân máu có thể áp dụng cho bênh nhân [[nội trú]] lẫn [[ngoại trú]]. Routine thẩm phân máu được tiến hành là thẩm phân máu ngoại trú facility, either a purpose built room in a [[hospital]] or a dedicated, stand alone clinic. Less frequently hemodialysis is done at [[home hemodialysis|home]]. Điều trị thẩm phân máu tại bệnh viện do nhân viên có chuyên môn như là y tá, chuyên viên kĩ thuật thực hiện; điều trị thẩm phân máu tại nhà có thể là các thành viên trong gia đình được tự đào tạo và hỗ trợ của các nhân viên huấn luyện.<ref>National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse guidance ''[http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/Kudiseases/pubs/choosingtreatment/index.htm Kidney Failure: Choosing a Treatment That's Right for You]''</ref> |
|||
==Nguyên tắc== |
|||
[[Image:Semipermeable membrane (svg).svg|thumb|250px|Màng bán thấm]] |
|||
Nguyên tắc thẩm phân máu is the same as other methods of [[dialysis]]; it involves [[diffusion]] of solutes across a semipermeable membrane. Hemodialysis utilizes [[Counter-current exchange|counter current flow]], where the dialysate is flowing in the opposite direction to [[blood flow]] in the [[extracorporeal]] circuit. Counter-current flow maintains the concentration gradient across the membrane at a maximum and increases the efficiency of the dialysis. |
|||
Fluid removal ([[ultrafiltration (renal)|ultrafiltration]]) is achieved by altering the [[hydrostatic pressure]] of the dialysate compartment, causing free water and some dissolved solutes to move across the membrane along a created pressure gradient. |
|||
The dialysis solution that is used may be a sterilized solution of mineral ions or comply with [[British Pharmacopoeia]]. [[Urea]] and other waste products, [[potassium]], and [[phosphate]] diffuse into the dialysis solution. However, concentrations of [[sodium]] and chloride are similar to those of normal [[Blood plasma|plasma]] to prevent loss. [[Sodium bicarbonate]] is added in a higher concentration than plasma to correct blood acidity. A small amount of glucose is also commonly used. |
|||
Note that this is a different process to the related technique of [[hemofiltration]]. |
|||
==Tham khảo== |
|||
{{reflist}} |
|||
==Xem thêm== |
|||
{{Commons category|Hemodialysis}} |
|||
* [http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/kudiseases/pubs/yourkidneys/ Your Kidneys and How They Work] - (American) National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), [[NIH]]. |
|||
* [http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/kudiseases/pubs/kidneyfailure/index.htm Treatment Methods for Kidney Failure] - (American) National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), [[NIH]]. |
|||
* [http://kidney.niddk.nih.gov/kudiseases/pubs/hemodialysis/ Treatment Methods for Kidney Failure: Hemodialysis] - (American) National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse, [[NIH]]. |
|||
* [http://www.ihatedialysis.com Online Community for Dialysis Patients by Dialysis Patients] |
|||
* [http://www.kidney.ca/english/publications/brochures/hemodialysis/hemodialysis.htm What is dialysis?] - Kidney Foundation of Canada |
|||
* [http://www.ceapir.org European Kidney Patients' Federation (CEAPIR)] |
|||
* [http://www.vph-arch.eu/ ARCH Project] - European research project for development of a model to simulate hemodynamic changes induced by AVF surgery and long-term adaptation. |
|||
{{Vascular surgery procedures}} |
|||
{{Toxicology}} |
|||
[[Category:Renal dialysis]] |
|||
[[Category:Toxicology treatments]] |
|||
[[Category:Membrane technology]] |
|||
Phiên bản lúc 09:12, ngày 26 tháng 12 năm 2013

Bài viết này là công việc biên dịch đang được tiến hành từ bài viết [[:FromLanguage:|]] từ một ngôn ngữ khác sang tiếng Việt. Bạn có thể giúp Wikipedia bằng cách hỗ trợ dịch và trau chuốt lối hành văn tiếng Việt theo cẩm nang của Wikipedia. |
Trong y học, Thẩm phân máu (haemodialysis hay haemodialysis) là phương pháp loại bỏ các chất thải như creatinine, urea, nước tự do từ máu được thực hiện bên ngoài cơ thể ở bệnh nhân suy thận. Thẩm phân máu là một trong ba phương pháp thay thế thận (hai phương pháp khác là phẩu thuật thay thận và thẩm phân phuc mạc). Phương pháp thay thế for extracorporeal separation of thành phần máu như huyết tương hoặc tế bào is apheresis.
Thẩm phân máu có thể áp dụng cho bênh nhân nội trú lẫn ngoại trú. Routine thẩm phân máu được tiến hành là thẩm phân máu ngoại trú facility, either a purpose built room in a hospital or a dedicated, stand alone clinic. Less frequently hemodialysis is done at home. Điều trị thẩm phân máu tại bệnh viện do nhân viên có chuyên môn như là y tá, chuyên viên kĩ thuật thực hiện; điều trị thẩm phân máu tại nhà có thể là các thành viên trong gia đình được tự đào tạo và hỗ trợ của các nhân viên huấn luyện.[1]
Nguyên tắc

Nguyên tắc thẩm phân máu is the same as other methods of dialysis; it involves diffusion of solutes across a semipermeable membrane. Hemodialysis utilizes counter current flow, where the dialysate is flowing in the opposite direction to blood flow in the extracorporeal circuit. Counter-current flow maintains the concentration gradient across the membrane at a maximum and increases the efficiency of the dialysis.
Fluid removal (ultrafiltration) is achieved by altering the hydrostatic pressure of the dialysate compartment, causing free water and some dissolved solutes to move across the membrane along a created pressure gradient.
The dialysis solution that is used may be a sterilized solution of mineral ions or comply with British Pharmacopoeia. Urea and other waste products, potassium, and phosphate diffuse into the dialysis solution. However, concentrations of sodium and chloride are similar to those of normal plasma to prevent loss. Sodium bicarbonate is added in a higher concentration than plasma to correct blood acidity. A small amount of glucose is also commonly used.
Note that this is a different process to the related technique of hemofiltration.
Tham khảo
- ^ National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse guidance Kidney Failure: Choosing a Treatment That's Right for You
Xem thêm
| Wikimedia Commons có thêm hình ảnh và phương tiện truyền tải về Thẩm phân máu. |
- Your Kidneys and How They Work - (American) National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), NIH.
- Treatment Methods for Kidney Failure - (American) National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), NIH.
- Treatment Methods for Kidney Failure: Hemodialysis - (American) National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse, NIH.
- Online Community for Dialysis Patients by Dialysis Patients
- What is dialysis? - Kidney Foundation of Canada
- European Kidney Patients' Federation (CEAPIR)
- ARCH Project - European research project for development of a model to simulate hemodynamic changes induced by AVF surgery and long-term adaptation.
