Bang và lãnh thổ liên bang của Ấn Độ
(Đổi hướng từ Bang và lãnh thổ của Ấn Độ)
| Bang và lãnh thổ liên bang của Ấn Độ | |
|---|---|
<maplink>: Không thể phân tích mã JSON: Lỗi ký tự điều khiển, có lẽ đã mã hóa không chính xác | |
| Thể loại | Federated state |
| Vị trí | Công hòa Ấn Độ |
| Số lượng còn tồn tại | 29 Bang 7 lãnh thổ liên bang |
| Dân số | Bang: Min:610,577 Sikkim –Max:199,812,341 Uttar Pradesh Lãnh thổ liên bang: 64,473 Lakshadweep – 16,787,941 National Capital Territory |
| Diện tích | Bang: Min:3.702 km2 (1.429 dặm vuông Anh) Goa –Max:342.269 km2 (132.151 dặm vuông Anh) Rajasthan Lãnh thổ liên bang: Min:32 km2 (12 dặm vuông Anh) Lakshadweep – Max:8.249 km2 (3.185 dặm vuông Anh) Andaman and Nicobar Islands |
| Hình thức chính quyền | State governments, Union Government (Union territories) |
| Đơn vị hành chính thấp hơn | Huyện, Phân cấp hành chính Ấn Độ |
Ấn Độ là một quốc gia liên bang, gồm 29 bang và 7 lãnh thổ liên bang. Các bang và lãnh thổ liên bang được phân chia hành chính thành các huyện và đơn vị hành chính dưới huyện.
Hiến pháp Ấn Độ phân chia quyền lực lập pháp và hành pháp giữa Nhà nước liên bang với các bang và vùng lãnh thổ.[1]
Lịch sử[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
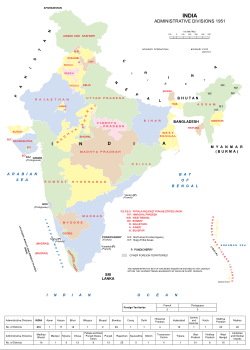
Tiền độc lập[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
Tiểu lục địa Ấn Độ được nhiều dân tộc khác nhau cai trị trong suốt thời kỳ lịch sử, mỗi chính quyền đều đều sử dụng những cách phân chia hành chính riêng.[2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10]
Danh sách[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
Bang[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
| Bang | ISO 3166-2:IN | Biển số xe | Thủ phủ | Thành phố lớn nhất | Thành lập | Dân số[11] | Diện tích (km²) |
Ngôn ngữ chính thức[12] |
Ngôn ngữ địa phương phổ biến[12] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pradesh | IN-AP | AP | Hyderabad (de jure) Amaravati (de facto) Note 1[13][14] |
Visakhapatnam | ngày 1 tháng 10 năm 1953 | 49,506,799 | 160,205 | Telugu | — |
| Arunachal Pradesh | IN-AR | AR | Itanagar | ngày 20 tháng 2 năm 1987 | 1,383,727 | 83,743 | Anh | — | |
| Assam | IN-AS | AS | Dispur | Guwahati | ngày 26 tháng 1 năm 1950 | 31,205,576 | 78,550 | Assam | — |
| Bihar | IN-BR | BR | Patna | ngày 26 tháng 1 năm 1950 | 104,099,452 | 99,200 | Hindi | Urdu | |
| Chhattisgarh | IN-CT | CG | Naya Raipur | Raipur | ngày 1 tháng 11 năm 2000 | 25,545,198 | 135,194 | Hindi | — |
| Goa | IN-GA | GA | Panaji | Vasco da Gama | ngày 30 tháng 5 năm 1987 | 1,458,545 | 3,702 | Konkani | Marathi |
| Gujarat | IN-GJ | GJ | Gandhinagar | Ahmedabad | ngày 1 tháng 5 năm 1960 | 60,439,692 | 196,024 | Gujarati | — |
| Haryana | IN-HR | HR | Chandigarh | Faridabad | ngày 1 tháng 11 năm 1966 | 25,351,462 | 44,212 | Hindi | Punjabi[15][16] |
| Himachal Pradesh | IN-HP | HP | Shimla (Summer)
Dharamshala (Winter) |
Shimla | ngày 25 tháng 1 năm 1971 | 6,864,602 | 55,673 | Hindi | English |
| Jammu and Kashmir | IN-JK | JK | Srinagar (Summer) Jammu (Winter) |
Srinagar | ngày 26 tháng 1 năm 1950 | 12,541,302 | 222,236 101,387Note 2 |
Urdu | — |
| Jharkhand | IN-JH | JH | Ranchi | Jamshedpur | ngày 15 tháng 11 năm 2000 | 32,988,134 | 74,677 | Hindi | Urdu[17] |
| Karnataka | IN-KA | KA | Bangalore | ngày 1 tháng 11 năm 1956 | 61,095,297 | 191,791 | Kannada | — | |
| Kerala | IN-KL | KL | Thiruvananthapuram | Kochi | ngày 1 tháng 11 năm 1956 | 33,406,061 | 38,863 | Malayalam | — |
| Madhya Pradesh | IN-MP | MP | Bhopal | Indore | ngày 1 tháng 11 năm 1956 | 72,626,809 | 308,252 | Hindi | — |
| Maharashtra | IN-MH | MH | Mumbai | ngày 1 tháng 5 năm 1960 | 112,374,333 | 307,713 | Marathi | — | |
| Manipur | IN-MN | MN | Imphal | ngày 21 tháng 1 năm 1972 | 2,855,794 | 22,347 | Meitei | English | |
| Meghalaya | IN-ML | ML | Shillong | ngày 21 tháng 1 năm 1972 | 2,966,889 | 22,720 | English | Khasi[a] | |
| Mizoram | IN-MZ | MZ | Aizawl | ngày 20 tháng 2 năm 1987 | 1,097,206 | 21,081 | English, Hindi, Mizo | — | |
| Nagaland | IN-NL | NL | Kohima | Dimapur | ngày 1 tháng 12 năm 1963 | 1,978,502 | 16,579 | English | — |
| Odisha | IN-OR | OD | Bhubaneswar | ngày 26 tháng 1 năm 1950 | 41,974,218 | 155,820 | Odia | — | |
| Punjab | IN-PB | PB | Chandigarh | Ludhiana | ngày 1 tháng 11 năm 1966 | 27,743,338 | 50,362 | Punjabi | — |
| Rajasthan | IN-RJ | RJ | Jaipur | ngày 1 tháng 11 năm 1956 | 68,548,437 | 342,269 | Hindi | English | |
| Sikkim | IN-SK | SK | Gangtok | ngày 16 tháng 5 năm 1975 | 610,577 | 7,096 | English | Bhutia, Gurung, Lepcha, Limbu, Manggar, Mukhia, Newari, Rai, Sherpa, Tamang | |
| Tamil Nadu | IN-TN | TN | Chennai | ngày 26 tháng 1 năm 1950 | 72,147,030 | 130,058 | Tamil | English | |
| Telangana | IN-TG | TS | HyderabadNote 1 | ngày 2 tháng 6 năm 2014 | 35,193,978[18] | 114,840[18] | Telugu, Urdu[19] | — | |
| Tripura | IN-TR | TR | Agartala | ngày 21 tháng 1 năm 1972 | 3,673,917 | 10,492 | Bengali, Kokborok, English | — | |
| Uttar Pradesh | IN-UP | UP | Lucknow | Kanpur | ngày 26 tháng 1 năm 1950 | 199,812,341 | 243,286 | Hindi | Urdu |
| Uttarakhand | IN-UT | UK | DehradunNote 3 | ngày 9 tháng 11 năm 2000 | 10,086,292 | 53,483 | Hindi | Sanskrit[20] | |
| West Bengal | IN-WB | WB | Kolkata | ngày 26 tháng 1 năm 1950 | 91,276,115 | 88,752 | Bengali, Nepali[b] | Hindi, Urdu, Santali, Odia and Punjabi | |
- ^Note 1 Andhra Pradesh was divided into two states, Telangana and a residual Andhra Pradesh on ngày 2 tháng 6 năm 2014.[21][22][23] Hyderabad, located entirely within the borders of Telangana, is to serve as the capital for both states for a period of time not exceeding ten years.[24] The Government of Andhra Pradesh and the Andhra Pradesh Legislature completed the process of relocating to temporary facilities in the envisaged new capital city Amaravati in early 2017.[13]
- ^Note 2 The area of Jammu and Kashmir is 222,236 km² according to Indian claims; thereof 101,387 km² are under Indian administration
- ^Note 3 Dehradun is the interim capital of Uttarakhand. The town of Gairsain is envisaged as the state's new capital.
Lãnh thổ liên bang[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
| Lãnh thổ liên bang | ISO 3166-2:IN | Vehicle code | Thủ phủ | Thành phố lớn nhất | Dân số[11] | Area (km²) |
Ngôn ngữ chính thức[12] |
Additional official languages[12] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | IN-AN | AN | Port Blair | 380,581 | 8,249 | Hindi, English | — | |
| Chandigarh | IN-CH | CH | Chandigarh | —[c] | 1,055,450 | 114 | English | — |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli | IN-DN | DN | Silvassa | 343,709 | 491 | Gujarati, Hindi | Marathi | |
| Daman and Diu | IN-DD | DD | Daman | 243,247 | 112 | English, Gujarati, Hindi, Konkani[d] | — | |
| Delhi | IN-DL | DL | New Delhi | —[e] | 16,787,941 | 1,490 | Hindi | Punjabi, Urdu[25] |
| Lakshadweep | IN-LD | LD | Kavaratti | 64,473 | 32 | English | Hindi | |
| Puducherry | IN-PY | PY | Pondicherry | 1,247,953 | 492 | English,[26] Tamil | Malayalam, Telugu | |
Các bang trước đây[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
| Bản đồ | Bang | Thủ phủ | Năm | Bang hiện trạng |
|---|---|---|---|---|
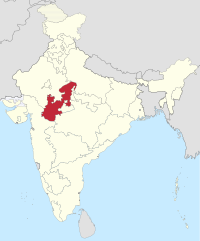
|
Madhya Bharat | Gwalior (winter) Indore (summer) |
1947–1956 | Madhya Pradesh |
| Bang Liên hiệp phía Đông (Eastern States Union) |
Raipur | 1947–1948 | Bihar, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh | |

|
Madras State | Madras | 1950–1969 | Tamil Nadu |

|
Mysore State | Mysore | 1947–1973 | Karnataka |

|
Bang Liên hiệp Patiala và Đông Punjab (Patiala and East Punjab States Union) | Patiala | 1948–1956 | Punjab, India |
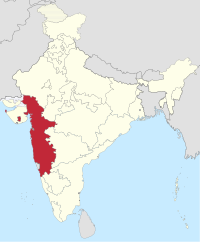
|
Bombay State | Bombay | 1947–1960 | Maharashtra, Gujarat |

|
Bhopal State | Bhopal | 1949–1956 | Madhya Pradesh |
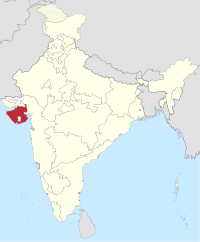
|
Saurashtra | Rajkot | 1948–1956 | Bombay State |

|
Coorg State | Madikeri | 1950–1956 | Mysore State |

|
Travancore-Cochin | Trivandrum | 1949–1956 | Kerala, Madras State |
| Hyderabad State | Hyderabad | 1948–1956 | Andhra Pradesh | |
|
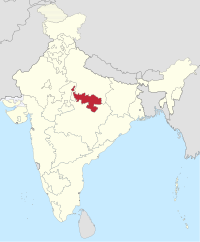
Vindhya Pradesh | Rewa | 1948–1956 | Madhya Pradesh |
|
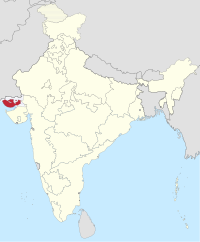
Kutch State | Bhuj | 1947–1956 | Bombay State |
|
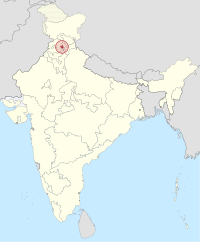
Bilaspur State | Bilaspur | 1948–1954 | Himachal Pradesh |
|
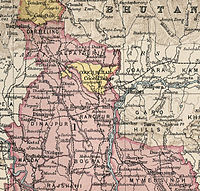
Cooch Behar State | Cooch Behar | 1949 | West Bengal |
|
Ajmer State | Ajmer | 1947–1956 | Rajasthan |
Xem thêm[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
- Phân cấp hành chính Ấn Độ
- Huyện của Ấn Độ
- Xã (Ấn Độ)
- Đô thị ở Ấn Độ
- Thành phố ở Ấn Độ
- Thị trấn ở Ấn Độ
- Vùng (Ấn Độ)
- ISO 3166-2:IN
Ghi chú[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
- ^ Khasi language has been declared as the Additional Official Language for all purposes in the District, Sub-Division and Block level offices of the State Government located in the Districts of Khasi-Jaintia Hills of Meghalaya.
- ^ Bengali and Nepali are the Official Languages in Darjeeling and Kurseong sub-divisions of Darjeeling district.
- ^ Chandigarh is both a city and a union territory.
- ^ It has also been informed that the communication with States/Centre has to be made in Hindi/English.
- ^ Delhi is both a city and a union territory.
Chú thích[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
- ^ "Article 73 broadly stated, provides that the executive power of the Union shall extend to the matters with respect to which Parliament has power to make laws. Article 162 similarly provides that the executive power of a State shall extend to the matters with respect to which the Legislature of a State has power to make laws. The Supreme Court has reiterated this position when it ruled in the Ramanaiah case that the executive power of the Union or of the State broadly speaking, is coextensive and coterminous with its respective legislative power." Territoriality of executive powers of states in India, Balwant Singh Malik, Constitutional Law, 1998
- ^ Krishna Reddy (2003). Indian History. New Delhi: Tata McGraw Hill. ISBN 0-07-048369-8.
- ^ Ramesh Chandra Majumdar (1977). Ancient India. Motilal Banarsidass Publishers. ISBN 81-208-0436-8.
- ^ Romila Thapar (1966). A History of India: Part 1.
- ^ G. Bongard-Levin (1984). A History of India: Volume 1.
- ^ Gupta Dynasty – MSN Encarta. Bản gốc lưu trữ ngày 1 tháng 11 năm 2009.
- ^ Nilakanta Sastri, K.A. (2002) [1955]. A history of South India from prehistoric times to the fall of Vijayanagar. New Delhi: Indian Branch, Oxford University Press. tr. 239. ISBN 0-19-560686-8.
- ^ Chandra, Satish. Medieval India: From Sultanate To The Mughals. tr. 202.
- ^ “Regional states, c. 1700–1850”. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
- ^ Grewal, J. S. (1990). “Chapter 6: The Sikh empire (1799–1849)”. The Sikh empire (1799–1849). The New Cambridge History of India. The Sikhs of the Punjab. Cambridge University Press. Bản gốc lưu trữ ngày 16 tháng 2 năm 2012. Truy cập ngày 7 tháng 11 năm 2017.
- ^ a b “List of states with Population, Sex Ratio and Literacy Census 2011”.
- ^ a b c d “Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 50th report (July 2012 to June 2013)” (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. Bản gốc (pdf) lưu trữ ngày 8 tháng 7 năm 2016. Truy cập ngày 14 tháng 1 năm 2015.
- ^ a b http://www.gulte.com/news/56377/After-2200-Years-Amaravati-Gets-Back-Power
- ^ “Bản sao đã lưu trữ”. Bản gốc lưu trữ ngày 3 tháng 8 năm 2017. Truy cập ngày 7 tháng 11 năm 2017.
- ^ “Haryana grants second language status to Punjabi”. Hindustan Times. ngày 28 tháng 1 năm 2010. Bản gốc lưu trữ ngày 3 tháng 9 năm 2015. Truy cập ngày 7 tháng 11 năm 2017.
- ^ “Punjabi gets second language status in Haryana”. Zee news. ngày 28 tháng 1 năm 2010.
- ^ “Bản sao đã lưu trữ”. Bản gốc lưu trữ ngày 25 tháng 2 năm 2021. Truy cập ngày 7 tháng 11 năm 2017.
- ^ a b “Telangana State Profile” (PDF). Telangana government portal. tr. 34. Truy cập ngày 11 tháng 6 năm 2014.
- ^ “Urdu Gets First Language Status”.
- ^ “Sanskrit: Reviving the language in today’s India – Livemint”.
- ^ “Bifurcated into Telangana State and residual Andhra Pradesh State”. The Times Of India. ngày 2 tháng 6 năm 2014.
- ^ “The Gazette of India: The Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act, 2014” (PDF). Ministry of Law and Justice. Government of India. ngày 1 tháng 3 năm 2014. Bản gốc (PDF) lưu trữ ngày 4 tháng 3 năm 2014. Truy cập ngày 23 tháng 4 năm 2014.
- ^ “The Gazette of India: The Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act, 2014 Sub-section” (PDF). ngày 4 tháng 3 năm 2014. Truy cập ngày 23 tháng 4 năm 2014.
- ^ Sanchari Bhattacharya (ngày 1 tháng 6 năm 2014). “Andhra Pradesh Minus Telangana: 10 Facts”. NDTV.
- ^ “Official Language Act 2000” (PDF). Government of Delhi. ngày 2 tháng 7 năm 2003. Bản gốc (PDF) lưu trữ ngày 4 tháng 3 năm 2016. Truy cập ngày 17 tháng 7 năm 2015.
- ^ http://www.lawsofindia.org/pdf/puducherry/1965/1965Pondicherry3.pdf
Tham khảo[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]
- Maps of the Historical Territorial Evolution of the States of India Lưu trữ 2015-05-07 tại Wayback Machine
- Official Government of India website: States and Union Territories
Bản mẫu:States and Union Territories of India Bản mẫu:Geography of India

